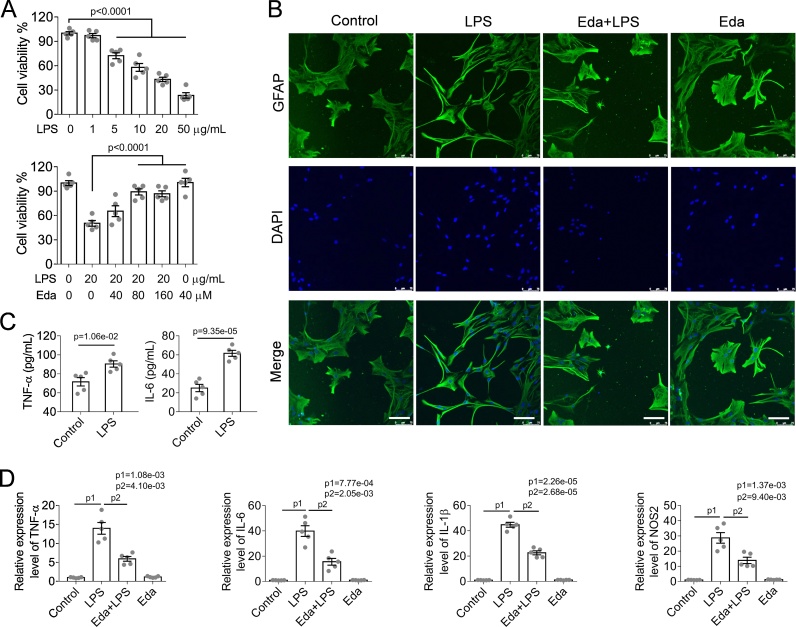
Fig. 3.
Edaravone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced astrocyte activation and inflammation.
(A) LPS inhibited cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner. Eda preserved cell viability from LPS-induced cytotoxicity. (B) Eda effectively mitigated LPS-induced astrocyte activation and inflammation, suggesting by immuno-labeling of GFAP. Scale bar, 100 μm. LPS (20 μM)-treated astrocytes showed shrunk nuclei (visualized by DAPI staining of DNA) and increase in cell numbers with slender outgrowth and dense branching compared with their normal counterparts. However, Eda administration (80 μM) alleviated LPS-induced morphological changes in astrocytes. (C) Increased expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 that determined by ELISA confirmed the induction of astrocyte activation and inflammation by LPS (20 μg/mL). Unpaired t-test with Welch's correction was performed to calculate the significance of intergroup difference, n = 5. (D) Eda (80 μM) alleviated LPS-induced astrocyte activation and inflammation by alleviating the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and NOS2. The relative mRNA expression level of the gene was normalized to β-actin.