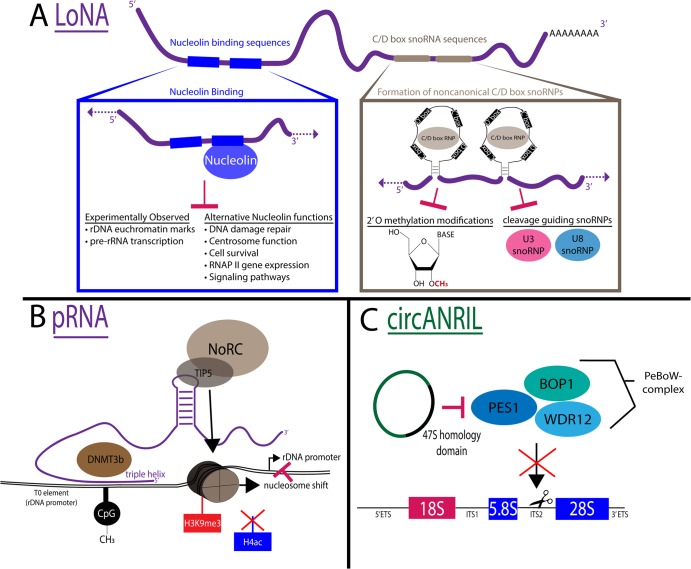
Figure 5. Examples of molecular mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) involved in ribosome biogenesis.
(A) Long nucleolar RNA (LoNA) is a multifunctional polyadenylated lncRNA that regulates pre-rRNA transcription, modification, and processing. (Left) It contains two nucleolin binding sequences (blue), one of which is functional to bind and inhibit nucleolin (blue) function. (Right) It contains two C/D box small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) sequences that are able to form noncanonical C/D box small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (snoRNPs) (gray) to inhibit modification and processing of the pre-rRNA. (B) pRNA is a multifunctional lncRNA that regulates ribosomal DNA (rDNA) chromatin modifications. (Left) It forms a DNA:RNA triple helix with the T0 element of the rDNA promoter to recruit the chromatin modifier DNMT3b (brown) to methylate CpG (black). (Right) It contains a stem-loop structure that interacts with TIP5 (gray) the large subunit of the nucleolar remodeling complex (NoRC) (brown) to promote H3K9me3 histone methylations (red), remove H4ac acetylation modifications (blue), and cause a nucleosome shift to block rDNA promoter access. (C) circANRIL (green) binds PeBoW complex (PES1, BOP1, WDR12,) (green/blue) to inhibit pre-rRNA processing of internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) through 47S homology domain (black).