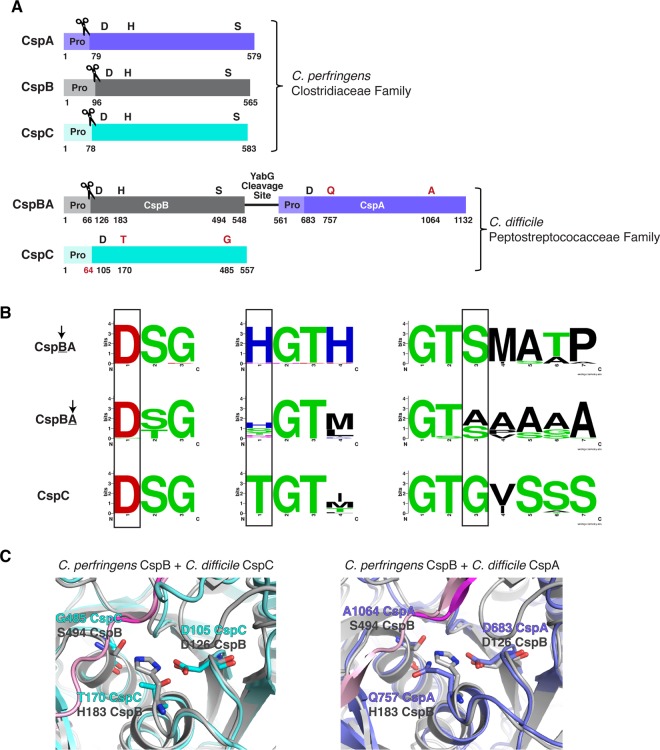
Figure 1. Csp family subtilisin-like serine proteases in the Clostridia.
(A) Schematic of the active Csp proteases encoded by C. perfringens, CspA, CspB and CspC, compared with Clostridiodes difficile Csp proteins, where an active CspB protease is fused to an inactive CspA pseudoprotease domain, and CspC is also a pseudoprotease. ‘Pro' denotes the prodomain that functions as an intramolecular chaperone. The C-terminal residue of the prodomains that have been mapped are shown below the schematic [27,31]. The catalytic triad residues, aspartic acid (D), histidine (H) and serine (S), are shown in black; pseudoactive site residues are shown in red. The scissor icon marks the autoprocessing sites of the Csp family members that are catalytically active, which separates the prodomain from the subtilase domain. The predicted site that would be cleaved by autoprocessing of the CspC pseudoprotease based on the CspC structure [30] is also shown in red. The YabG cleavage site [42] between CspB and CspA is shown. (B) Sequence logos of the catalytic triad residue regions for CspBA and CspC of the Peptostreptococcaceae family. Regions shown correspond to the MEROPS protease database [53] definitions for the peptidase family S8A. Information regarding gene location and accession number for the proteins is included in the sequence logo analysis provided in Supplemental Table S3. (C) Cartoon model of the active/ pseudoactive site regions of either C. perfringens CspB (grey, PDB 4I0W) aligned to C. difficile CspC (cyan, PBD 6MW4) or CspB (grey) aligned to C. difficile CspA iTasser model (periwinkle), active site region. The cleaved prodomain of CspB is shown in dark magenta compared with the uncleaved prodomain of CspC (light pink) and CspA prodomain (light pink).