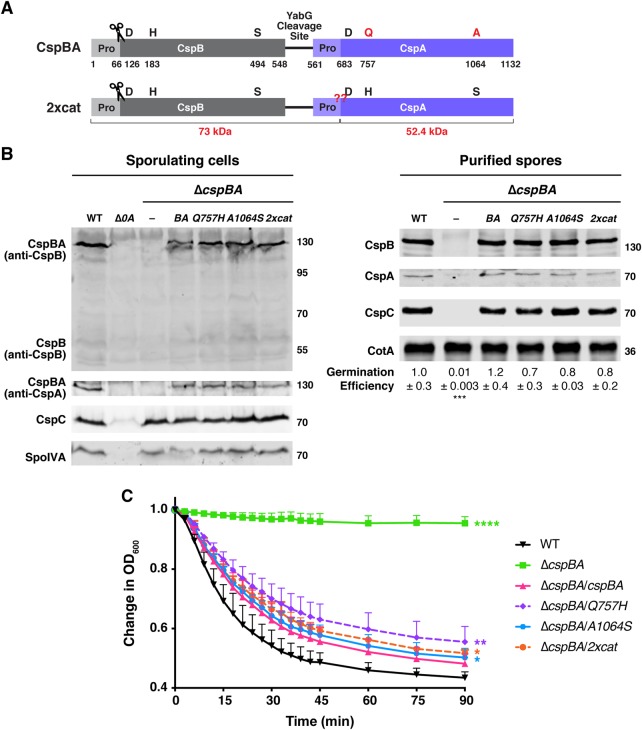
Figure 4. Restoring CspA's catalytic triad in C. difficile does not resurrect its protease activity or impact CspBA levels or function.
(A) Schematic of the CspBA fusion protein, where an active CspB protease is fused to an inactive CspA pseudoprotease domain. ‘Pro' denotes the prodomain. The C-terminal residue of the CspB prodomain following autoprocessing (denoted by the scissors) is shown [27]. Catalytic triad residues, aspartic acid (D), histidine (H) and serine (S), are shown in black; CspA pseudoactive site residues are shown in red. The CspA prodomain was identified using structural modeling [52]; the predicted cleavage site is shown in red below the schematic. The red ‘??' indicates the site where CspBA2xcat would be expected to undergo autoprocessing, if restoring the catalytic triad to CspA ‘resurrected' CspA protease activity. This would be expected to release the CspA subtilase domain (52.4 kDa) from the CspBA fusion protein, which also undergoes CspB-mediated autoprocessing. The YabG cleavage site [42] between CspB and CspA is shown. (B) Western blot analyses of CspB(A) and CspC in sporulating cells and purified spores from wild type 630Δerm-p, ΔcspBA, and ΔcspBA complemented with either wild-type cspBA or the cspBA catalytic variant (2xcat). CspBA was detected with anti-CspB and anti-CspA antibodies. Δspo0A (Δ0A) was used as a negative control for sporulating cells. SpoIVA was used as a loading control for sporulating cells. CotA was used as a loading control for purified spores. The germination efficiency of spores from the indicated strains plated on BHIS medium containing 0.1% taurocholate is shown relative to wild type. The mean and standard deviations shown are based on multiple technical replicates performed on two independent spore purifications. Statistical significance relative to wild type was determined using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey's test. (C) Change in the OD600 in response to germinant of CspBA catalytic mutant spores relative to wild-type spores. ΔcspBA mutant spores serve as a negative control. Purified spores were resuspended in BHIS broth, and germination was induced by adding taurocholate (1% final concentration). The ratio of the OD600 of each strain at a given time point relative to the OD600 at time zero is plotted. The mean of three independent assays from at least two independent spore preparations are shown. The error bars indicate the standard deviation for each time point measured. Statistical significance relative to wild type was determined using a two-way ANOVA and Tukey's test. **** P < 0.0001, *** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01, * P < 0.05.