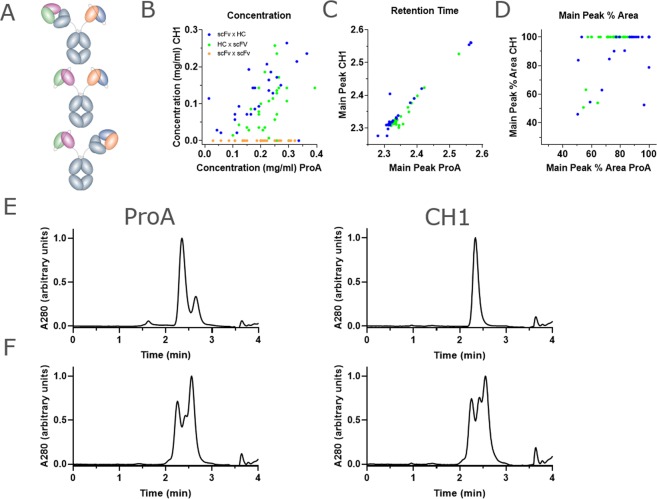
Figure 4.
Analysis of BsAbs generated by DNA imbalance and CH1 capture using high-throughput methods. (A) Comparison of the total yield of antibody from CH1 capture vs protein A capture showing that over-expression of the scFv-Fc arm generally results in saturation of the HC arm, allowing CH1 capture of highly pure BsAb. The two “bipod” format BsAbs (HC × scFv-Fc or scFv × HC) are indicated in blue and green. scFv-Fc × scFv-Fc format bipods are shown in orange. (B) Comparison of the elution time of the main peak from CH1 capture vs protein A capture showing that the main peak is generally represented by target heterodimer and is consistent between methods. (C) Comparison of the % of the total protein population represented by the main peak from CH1 capture vs protein A capture showing that CH1 capture generally results in highly pure target BsAb. (D,E) Analytical SEC analysis of two proteins which illustrate the requirement for over-expression of the scFv-Fc arm. In D, excess DNA of the scFv-Fc arm results in over-expression of this component, leading to saturation of the HC-only species during expression. After protein A capture, CH1 capture retains only target BsAb. In E, over-expression of the HC component prevents its saturation with scFv-Fc arm, and prevents isolation of the target BsAb after protein A capture.