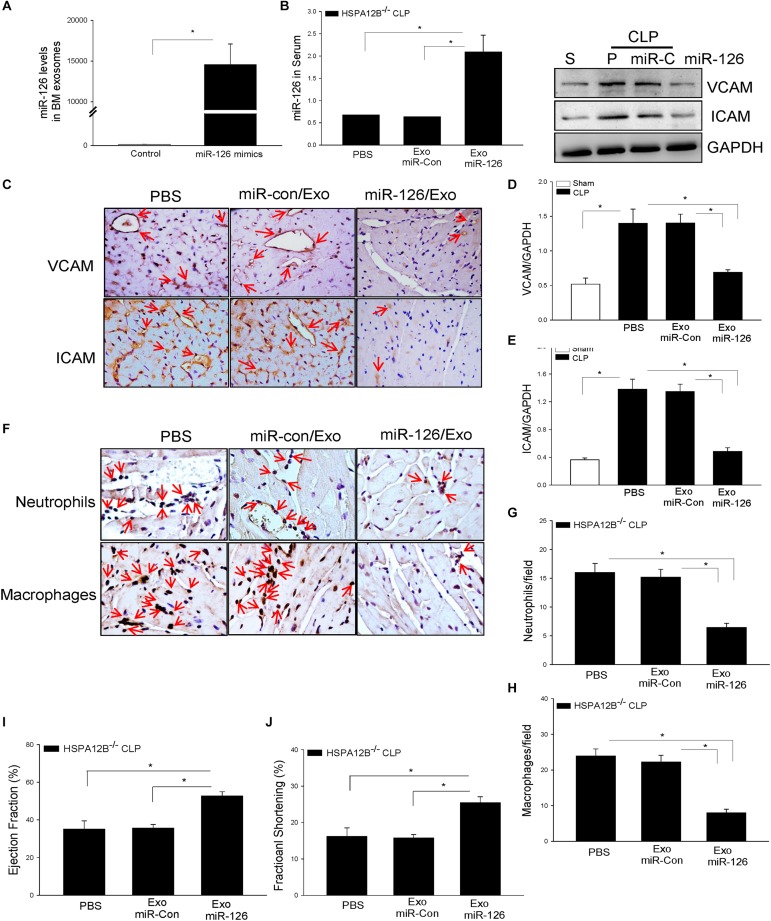
FIGURE 6.
MicroRNA-126 carried by exosomes derived from bone marrow stromal cells suppressed adhesion molecule expression in the myocardium of HSPA12B–/– septic mice. Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) were isolated from HSPA12B–/– mice and transfected with 40 nmol/L scrambled miR-control or miR-126 mimics at the fourth to seventh generation. Twenty-four hours after transfection, exosomes were isolated from supernatants. (A) The levels of miR-126 in exosomes were examined qPCR. (B) HSPA12B–/– mice were transfected with exosomes loaded with miR-126 mimic or scrambled miR-control through the right carotid artery immediately before induction of CLP sepsis. Serum miR-126 levels were examined by qPCR 6 h after CLP. (C) VCAM-1 and ICAM1 expressions in the heart tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry staining with anti–VCAM-1 and anti–ICAM-1 antibodies. (D,E) Western blot analysis of VCAM-1 and ICAM1 levels in the myocardium of HSP12B–/– septic mice (n = 6–9/group). (F) The accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages in the myocardium was examined by immunohistochemistry with antineutrophil elastase antibody and antimacrophage antibody F4/80. (G,H) miR-126 carried by exosomes decreased the numbers of neutrophils (G) and macrophages (H) in the myocardium of HSPA12B–/– septic mice. (I,J) miR-126 carried by exosomes improves cardiac function (EF %, FS %) measured by echocardiography. n = 6–9/group for Western blot and n = 3/group for immunohistochemistry. *P < 0.05 compared with indicated groups. The immunohistochemistry staining was examined with bright field microscope (40×).