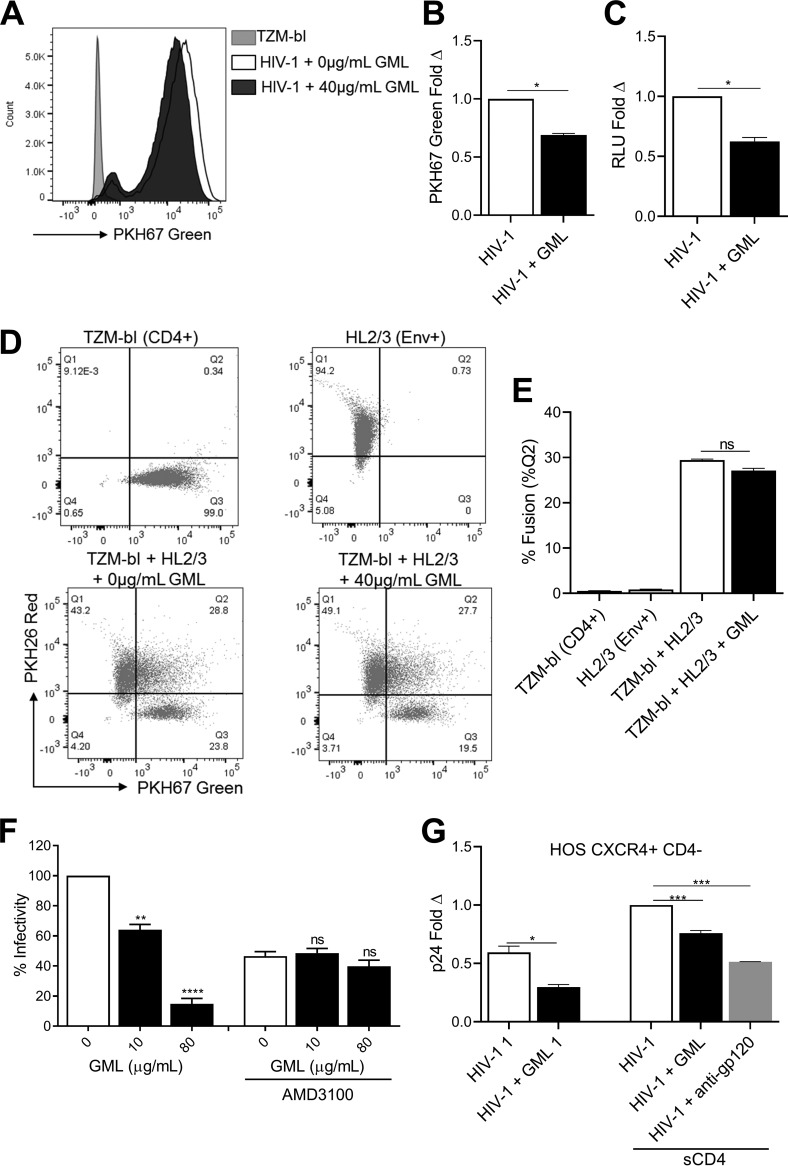
FIG 4.
GML restricts HIV-1 binding to coreceptor. Effects of GML on binding of green fluorescence-labeled HIV-1 in TZM-bl cells were determined. (A and B) Quantification of internalized virus following trypsin removal of surface virus as counts (C) and fold data (B). (C) TZM-bl luciferase (RLU) reporter activity. Cell-cell fusion of green fluorescence-labeled TZM-bl (CD4+) and red fluorescence-labeled HL2/3 (Env+) in the presence of GML. (D and E) Quantification of fused cells (%Quadrant 2) double-labeled red fluorescence positive and green fluorescence positive as scatterplots (D) and fusion data (E). (F) Infectivity after treatment of TZM-bl cells with CXCR4 (AMD3100) inhibitor for 1 h prior to infection and addition of GML at the time of HIV-1 inoculation. Vehicle-treated cells in the absence of inhibitor are set as the reference at 100%. TZM-bl infectivity was measured by luciferase reporter activity. (G) p24 content after HIV-1 was treated with soluble CD4 for 2 h prior to infection and addition of GML at the time of HIV-1 inoculation of HOS CXCR4+ CD4− cells. HIV-1 treated with soluble CD4 and vehicle control is set as the reference at a value of 1. Ethanol was used as a vehicle control. Statistics data were determined by comparing values from vehicle to values from treatment. Significance was determined by Student's t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Error bars represent SEM of results from three biological replicates. ns, not significant.