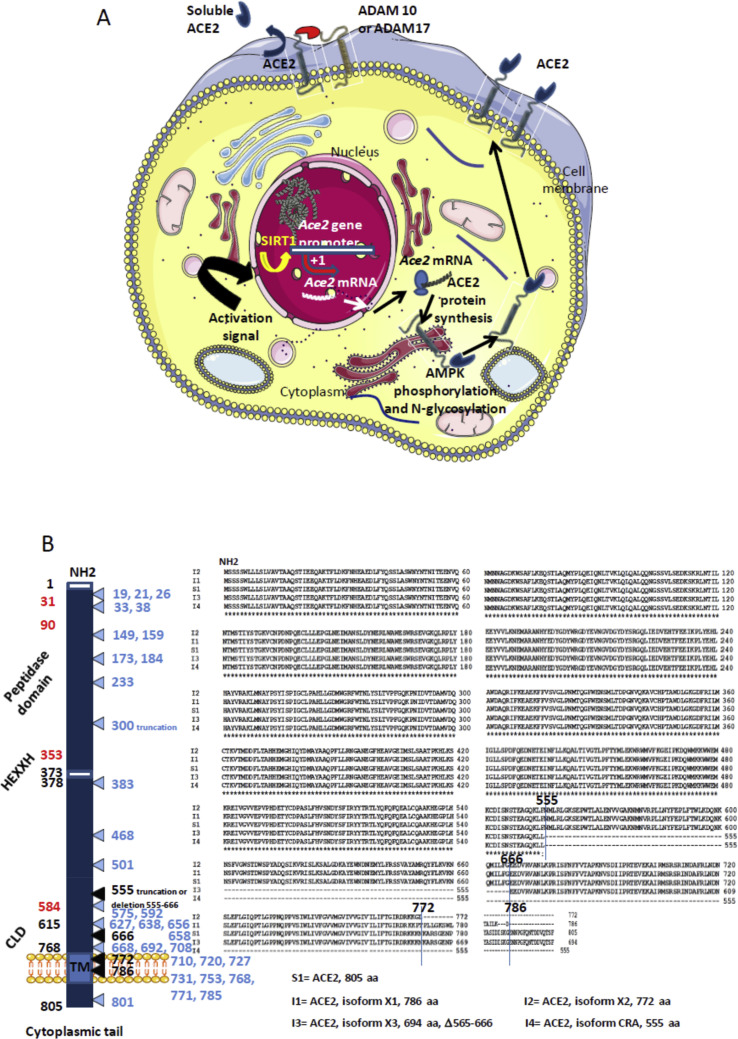
Figure 1.
A. Schematic representation of the regulation of ACE2. The transcription of the Ace2 gene is under control of the SIRT1 DNA-binding protein that binds the Ace2 gene promotor. Post-transcriptional regulation by miRNA (miRNA143, miRNA421) could occur (not shown). Following translation the newly synthesized ACE2 proteins are likely target of post-transcriptional modifications such as phosporylation of Ser680 by AMPK that enhances the stability of ACE2, and N-glycosylations. Once expressed at the cell membrane the ACE2 protein can be regulated by sheddases (ADAM10, ADAM17) that cleave the ACE2 extracellular domain and release a circulating soluble form sACE2 capable to interact with integrins (ITGB1). B. Schematic representation (left) of the ACE2 molecule and its major domains. The amino acids position is in black. Some of the amino acids important for viral tropism are in red (previous studies showed that residues 31, 41, and regions 82–84 and 353–357 are important for viral spike binding). Clustal Omega multiple sequence alignment (EMBL-EBI bioinformatic tool; Copyright © EMBL 2020) of human ACE2 and its different isoforms (right). The comparison of the reference Homo sapiens ACE2 protein sequence (S1=Genbank: BAB40370.1) with 9 others ACE2 sequences from the NCBI reference sequence database (S2=UniProtKB Q9BYF1.2; S3=NCBI NP_001358344.1; S4=NCBI NP_068576.1; S5= GenBank EAW98892.1; S6= GenBank AAH48094.2; S7= GenBank AAH39902.1; S8= GenBank AAO25651.1; S9= GenBank BAD99267.1; GenBank AAF99721.1), showed 100% amino acids identity (not shown). The Clustal MSA was also used for the comparison of the human ACE2 S1 sequence and available sequences of ACE2 isoforms: the isoform X1 (I1) = NCBI XP_011543851.1; isoform X2 (I2) = NCBI XP_011543853.1; isoform X3(I3) = NCBI XP_011543854.1; isoform CRA (I4) = GenBank EAW98891.1. The figure illustrates that these isoforms correspond to deletions in the CLD domain, or truncations in the transmembrane domain. A very elegant work by Cao and colleagues42 has recently analyzed 1700 ACE2 variants in search of ACE2 protein polymorphism. The mutations and truncations found by this team are shown in light blue.