Figure 3.
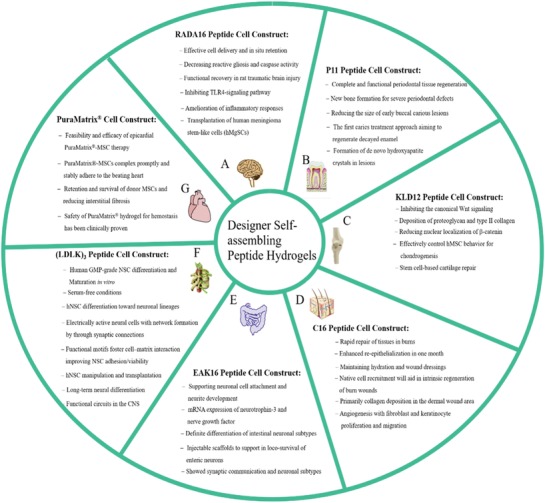
Schematic cell constructs are recently developed for tissue‐specific modeling, which is available or served as already tested tissue remodeling strategies in designer self‐assembling peptide hydrogels. A) Human stem cell‐based cell construct provides alternative options for peripheral nerve regeneration and repair strategies in RADA16‐I hydrogel,[ 65 ] in addition to the cell construct in EFK‐I hydrogel, which is effectively injectable cell delivery platform for intervertebral disc repair applications.[ 66b ] B) P11 peptide hydrogel directly indicates in situ clinical treatment benefit for early buccal carious lesions.[ 216 ] Other designer peptide hydrogels are the effective cell scaffolds for periodontal regeneration or dental pulp‐derived stem cell transplantation.[ 9b ] C) N‐cadherin mimetic peptide nanofiber hydrogel and KLD12 hydrogel are able to enhance cell‐to‐cell interactions by a tissue‐specific modeling strategy to support mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) commitment into the chondrogenic lineage.[ 171 , 217 ] D) Arg‐Gly‐Asp‐Ser (RGDS)‐modified peptide amphiphile (PA) hydrogel generate a type of instructive cell construct for the epidermis, neovascularization, and proliferation of fibroblasts.[ 218 ] E) Functionalized EAK16‐II hydrogels offer the tools to inject or dab the tissue‐specific cell construct onto intestinal areas affected by loss of loconeurons to treat the gastrointestinal disorders caused by the lack of specific neuronal subpopulations.[ 99 ] F) The hNSC‐seeded cell construct in (LDLK)3 hydrogel provides three translational possibilities in synthetic designer peptide scaffolds, GMP‐hNSCs, and serum‐free cultures in nanotechnology.[ 67 ] G) Instantly produced PuraMatrix hydrogel‐MSC complex is an advanced cell construct for innovative therapy in rat heart failure models,[ 85 ] since the feasibility and efficacy of Purastat hydrogel achieves the clinical approval in suture line hemostasis.[ 60 ] Panels (A–G) are reproduced with permission.[ 9b ] Copyright 2017, Elsevier Ltd.
