Figure 2.
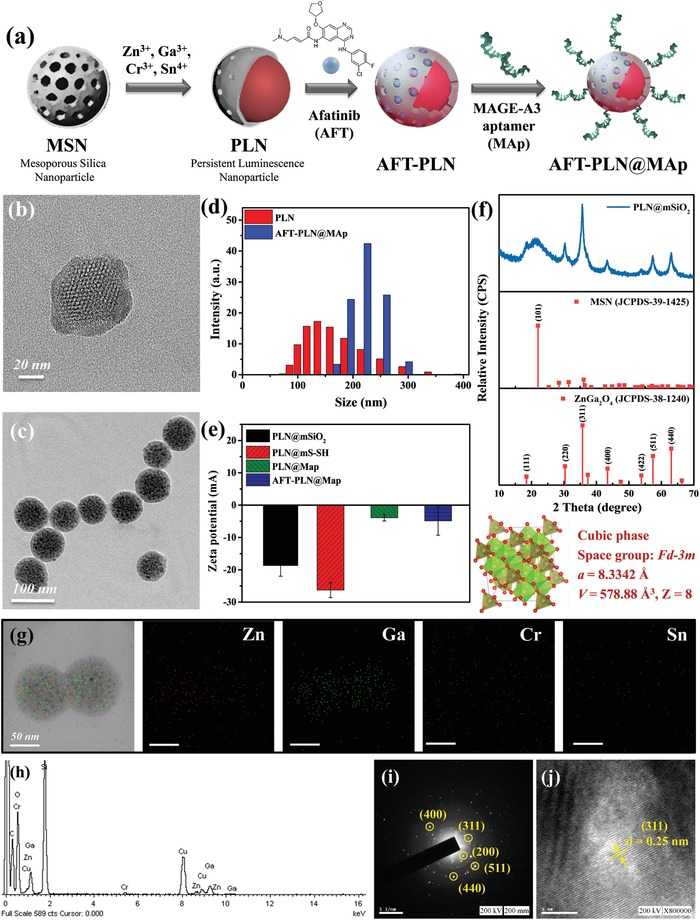
Basic characteristics of PLNs and the derivative PLNs. a) Schematic diagram of the synthetic AFT‐PLN@MAp procedure. This study first used mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) as a material template and added inorganic metal molecules to the core of the hole to form a PLN. After washing the metal ions, the AFT drug molecules are loaded and the aptamer is modified to form AFT‐PLN@MAp. Transmission electron microscopy images of b) MSN and c) PLNs, which form a deep black dot‐like ZGOCS structure in the MSN of the original hole structure. d) Dynamic light scattering and e) zeta potential data showing the degree of dispersion and surface electrical properties of the material, respectively. The PLN has a hydration radius of approximately 125 nm and an AFT‐PLN@MAp size of approximately 225 nm. Additionally, AFT‐PLN@MAp has a suitable degree and physiological charge of dispersion and a more concentrated particle size distribution. f) X‐ray powder diffraction (XRD) data. JCPDS‐38‐1240 has a crystal phase structure consistent with the synthesized AFT‐PLN@MAp. Energy‐dispersive X‐ray spectroscopy g) mapping and h) spectrum. The elemental structure of the material was tested using Zn, Ga, Cr, and Sn. Selected area (electron) diffraction data with i) specific area and j) d‐spacing were compared with the data collected by XRD, where the (311) characteristic peak is consistent with the XRD.
