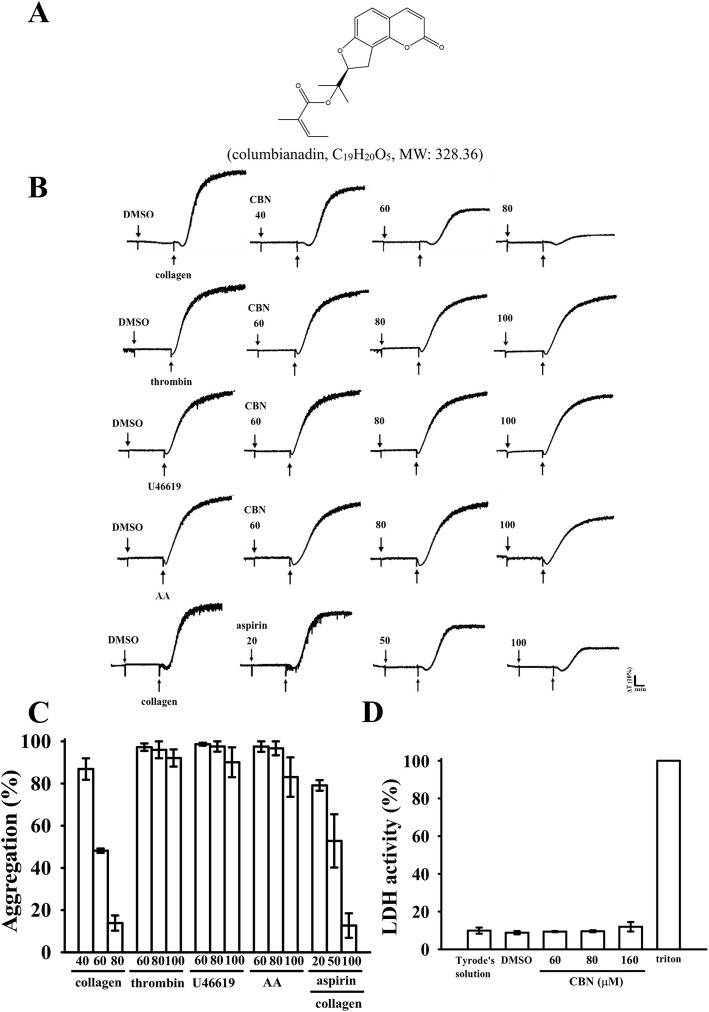
Fig. 1.
Inhibitory activities of columbianadin (CBN) on platelet aggregation and cytotoxicity stimulated by agonists. Washed human platelets (3.6 × 108 cells/mL) were preincubated with a solvent control (0.1% DMSO), CBN (40–100 μM) (a, chemical structure) or aspirin (20–100 μM) and subsequently treated with 1 μg/mL of collagen, 0.01 U/mL of thrombin, 1 μM U46619, or 60 μM of arachidonic acid (AA) to stimulate platelet aggregation (b). Concentration–response histograms of CBN in inhibition of platelet aggregation (%) (c). To assess the cytotoxicity (d), platelets were preincubated with the solvent control (0.1% DMSO) or CBN (60, 80, and 160 μM) for 20 min, and a 10-μL aliquot of the supernatant was deposited on a Fuji Dri-Chem slide LDH-PIII. Data (c and d) are presented as the means ± SEM (n = 4)