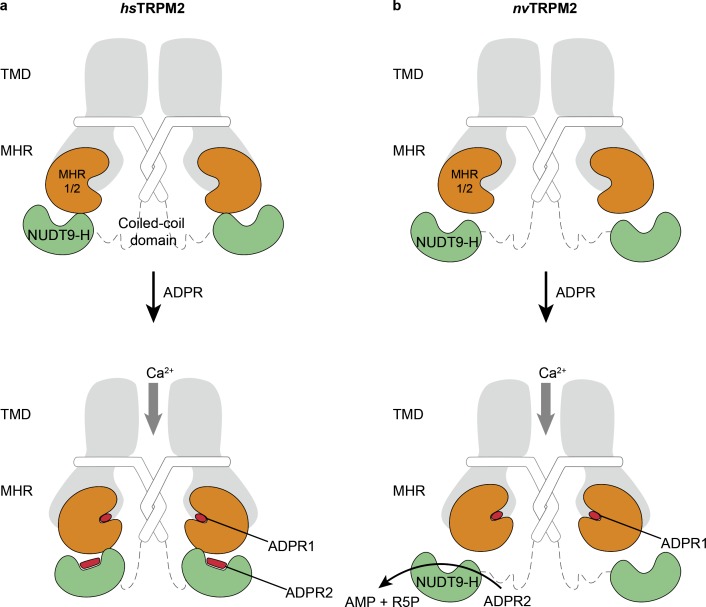
Figure 1.
ADPR binding sites in human TRPM2 (hsTRPM2) and an invertebrate TRPM2 from N. vectensis (nvTRPM2). (a) In hsTRPM2, binding of ADPR in both the N-terminal MHR1/2 domain and the C-terminal NUDT9-H domain is indispensable for channel activation. The ADPR1 is in a U-shape, while ADPR2 is in an extended shape. (b) In nvTRPM2, the channel activation requires only binding of ADPR into the MHR1/2 domain, while the NUDT9-H domain has only enzymatic activity to hydrolyze ADPR into AMP and R5P.