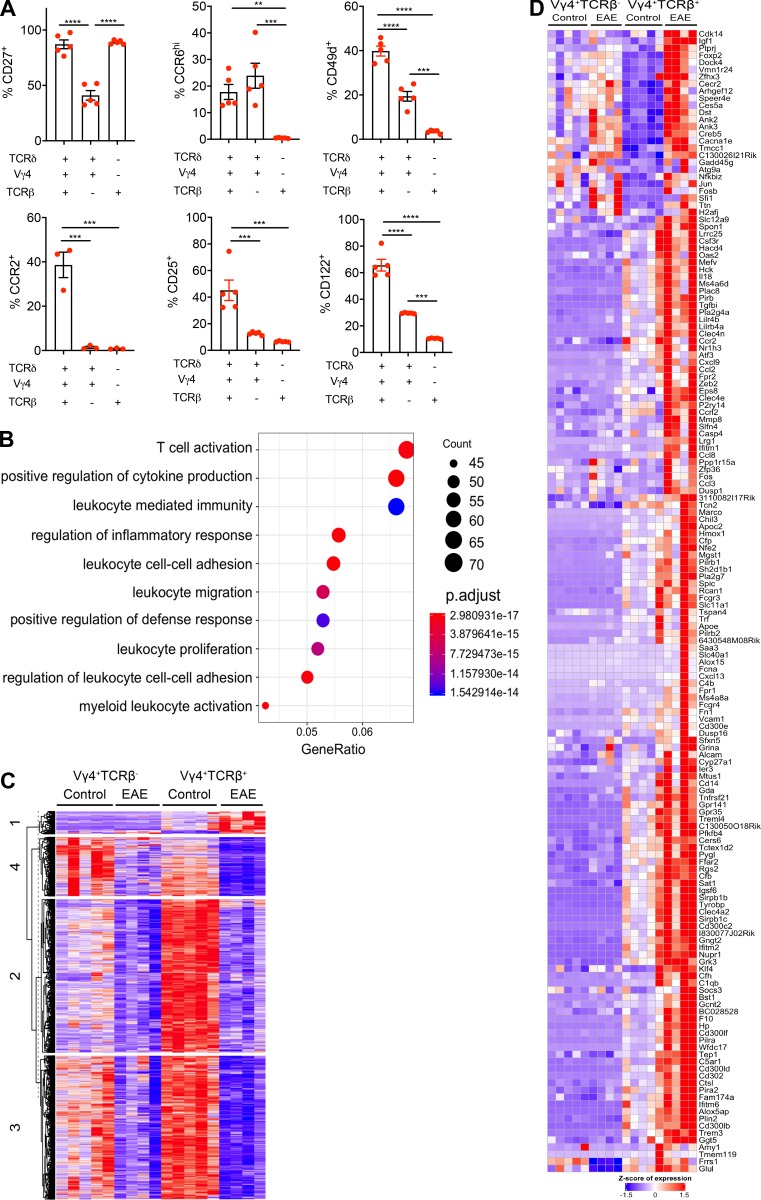
Figure S3.
Hybrid αβ-γδ T cells are transcriptomically distinct from conventional γδ T cells and express Th17-associated markers. (A) Enriched T cells isolated from the spleens and LNs of WT mice were stained ex vivo for CCR2, CCR6, CD25, CD27, CD49d, and CD122. Expression was determined on live CD3+ cells coexpressing various combinations of Vγ4, TCRδ, and TCRβ. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test for multiple comparisons. (B) Dot plot of the top 15 significantly enriched biological processes inferred from differentially up-regulated genes in Vγ4+TCRβ+ versus Vγ4+TCRβ– cells. Dot color represents the P-adjusted enrichment value, and dot size represents the number of genes within each enriched ontology. (C) Heatmap of all protein-coding genes that are differentially expressed in Vγ4+TCRβ+ or Vγ4+TCRβ– cells from mice with EAE versus naive mice (n = 2,686). Genes are clustered using k-means clustering and a cluster size of 4. (D) Heatmap of all protein-coding genes that are up-regulated in either Vγ4+TCRβ+ or Vγ4+TCRβ− cells from naive mice or mice with EAE (cluster 1 from Fig. S3 C, n = 158 genes). **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001, and ****, P < 0.0001.