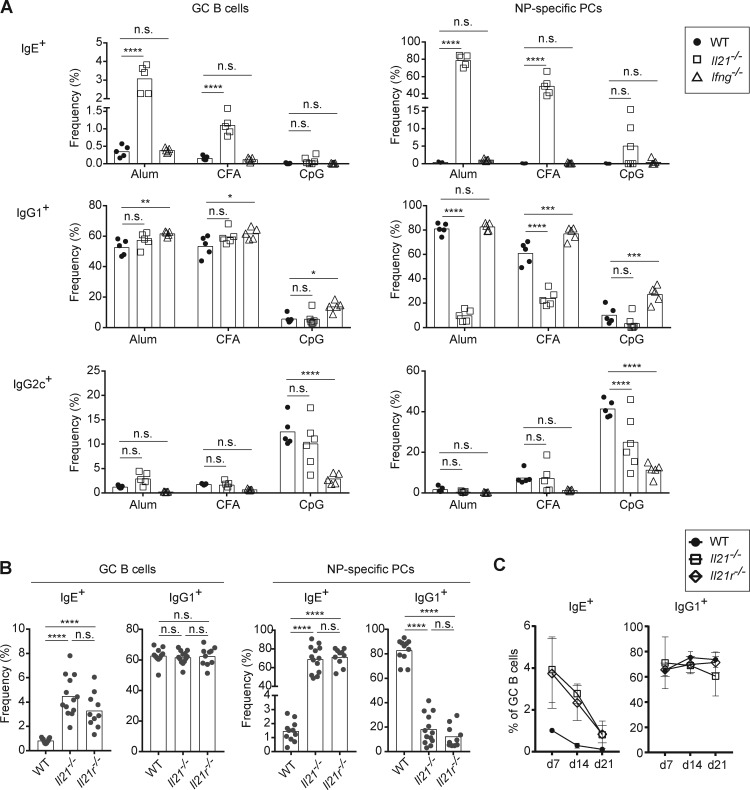
Figure 2.
IL-21, rather than IFN-γ, is a major suppressor of IgE responses in vivo. (A–C) Mice were immunized subcutaneously with NP-CGG with the indicated adjuvants (A) or alum adjuvant (B and C). Draining LNs were collected and analyzed 7 d (A and B) or 7–21 d (C) after immunization, and then cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to enumerate isotype-specific GC B cells and NP-specific PCs as in Fig. 1. (A) Frequency of IgE+, IgG1+, and IgG2c+ cells in the GC B cell and NP-specific PC compartments in WT, Il21−/−, and Ifng−/− mice. (B) Frequency of IgE+ and IgG1+ cells in the GC B cell and NP-specific PC compartments in WT, Il21−/−, and Il21r−/− mice. (C) Kinetic analysis of the frequency of IgE+ and IgG1+ B cells among GC B cells in WT, Il21−/−, and Il21r−/− mice. WT mice were B6/J (purchased from The Jackson Laboratory; A) or a mixture of purchased B6/J mice and WT mice on a B6 background bred in our colony (B and C). Dots represent individual mice. Bars represent the mean. n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test comparing each knockout to the WT group [A] or one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-tests for multiple comparisons [B]). Similar IgE and IgG1 responses as in A were observed in a separate experiment when mice were immunized with NP-CGG in alum (data not shown). Data in B are compiled from three experiments. Data in C at day 7 were from one experiment represented in B.