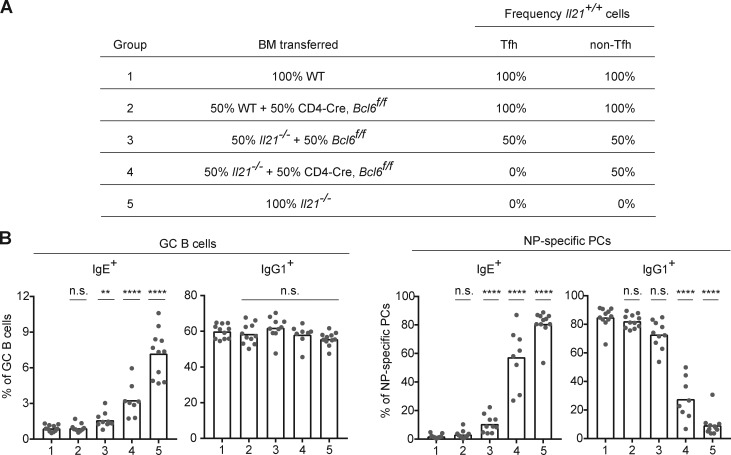
Figure 4.
IgE responses in vivo are inhibited by IL-21 derived primarily from Tfh cells. Draining LNs were collected 7 d after subcutaneous immunization with NP-CGG in alum adjuvant, and then cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to enumerate isotype-specific GC B cells and NP-specific PCs as in Fig. 1. (A) Groups of BM chimeras generated to test the impact of selective deficiency of IL-21 in Tfh cells. The indicated combinations of BM cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated Il21−/− mice. The expected frequencies of cells capable of IL-21 expression (frequency Il21+/+) in the Tfh and non-Tfh cell compartments in the resultant chimeras are indicated. Donor frequencies were confirmed in the chimeras by congenic markers as follows: WT BM was from a Boy/J (CD45.1) mouse bred in our colony. The Il21−/− BM was CD45.1, derived from backcrossing Il21−/− B6 to Boy/J congenic mice. The CD4-Cre, Bcl6f/f BM, and control Bcl6f/f BM were from littermates (with the CD45.2 congenic marker). The recipient mice were Il21−/− CD45.1/CD45.2. (B) Frequency of IgE+ and IgG1+ cells in the GC B cell and NP-specific PC compartments of the mixed BM chimeras generated as in A. Dots represent individual mice. Bars represent the mean. n.s., not significant; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test comparing each group to group 1). Data in B were pooled from two experiments.