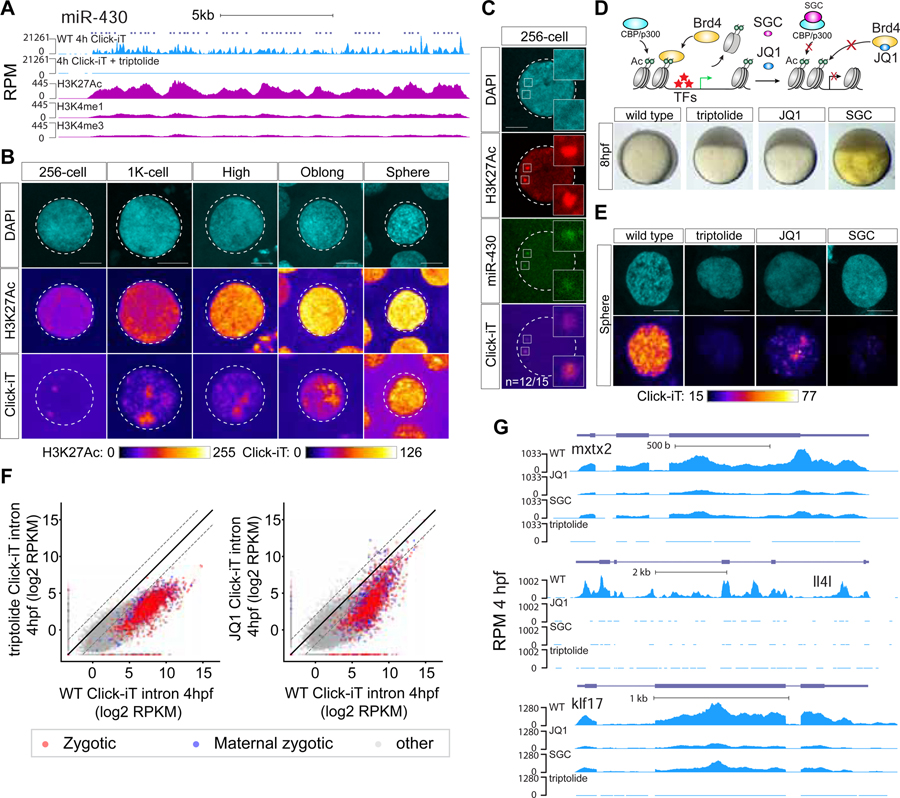
Figure 5. H3K27Ac correlates with transcriptional activation during ZGA.
(A) Genome tracks representing normalized Click-iT-seq signal and histone mark level at the miR-430 locus. ChIP-seq data (Bogdanovic et al., 2012). RPM for Click-iT-Seq/ChIP-Seq (STAR Methods). (B) Time resolved single nucleus confocal imaging analysis of H3K27Ac from 256-cell to sphere stage reveals a positive correlation with the level of Click-iT signal. Both H3K27Ac and Click-iT signal intensity are presented in a heatmap color scale. Scale bar represents 5 μm. (C) Single plane confocal image labeled for DAPI, H3K27Ac, dCas9-miR-430 and Click-iT. Note the co-localization of H3K27Ac with Click-iT labeled transcription activity at the miR-430 locus. (n=the fraction of analyzed nuclei that shows the same co-localization of H3K27Ac with Click-iT labeled transcription at the miR-430 locus as the representative nucleus, >3 independent embryos are imaged) Scale bar represents 5 μm. (D) Schematic illustrating the selective pharmacologic inhibition of the activity of the BET bromodomain proteins (BRD2–4) and CBP/P300 by JQ1 and SGC respectively (top). Embryos treated with JQ1 and SGC both arrest before gastrulation similar to those treated with triptolide, consistent with a loss of zygotic transcription (bottom) (Ac = H3K27 acetylation, TFs = transcription factors). (E) Click-iT imaging analysis in wild-type, triptolide, JQ1 and SGC treated embryos reveals a significant reduction in transcription by the treatment of JQ1 and SGC. Click-iT signal intensity is presented in a heatmap color scale. Scale bar represents 5 μm. (F) Biplot comparing intron expression levels of genes measured by Click-iT-seq in triptolide (left) and JQ1 (right) treated embryos with wild-type embryos at 4hpf. Dashed lines represent 4-fold change. (G) Genome tracks representing normalized Click-iT-seq signal measured at 4hpf in wild-type, triptolide, JQ1 and SGC treated embryos for examples of zygotic genes. RPM (STAR Methods). See also Figure S6.