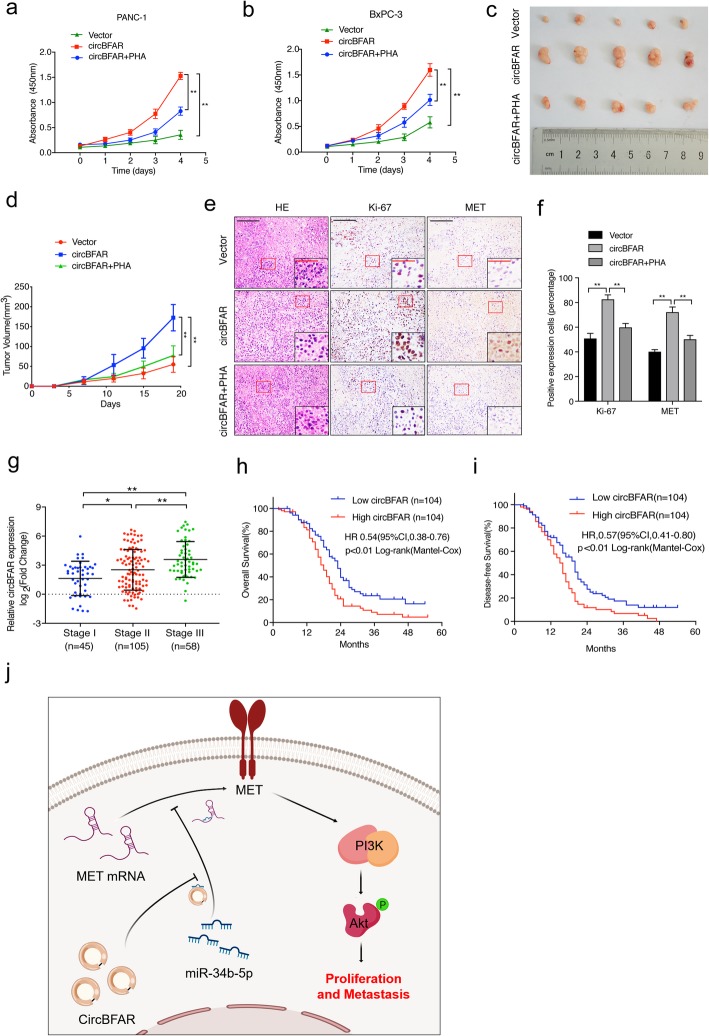
Fig. 9.
A MET inhibitor reverses the oncogenic effect induced by overexpression of circBFAR in vivo. a, b CCK-8 experiments showing that transfected circBFAR increased the proliferation ability of PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells; however, this function was reversed after treatment with the MET inhibitor PHA. c Representative images of subcutaneous xenograft tumors. d The volume of the tumors increased markedly after treatment with circBFAR when compared with the vector group, while treatment with PHA attenuated this effect. e, f Representative HE and IHC staining images of subcutaneous tumors revealed the relative protein levels of Ki-67 and MET in the different groups. The images were photographed at 100X or 400X (insert) magnification. Scale bar: black =200 μm; red =50 μm. g qRT-PCR analysis the expression of circBFAR in PDAC tissues with different TNM stages. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney U-test was used. h, i Kaplan-Meier curves for OS (h) and DFS (i) of patients with PDAC with low vs. high expression of circBFAR. The median circBFAR expression was used as the cutoff value. j Schematic illustration showing the suggestion mechanism by which circBFAR promotes proliferation and metastasis in PDAC via the miR-34b-5p/MET axis. Statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed t-tests for two group comparison, and one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s tests for multiple comparison. The error bars represent the standard deviations of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01