Figure 3.
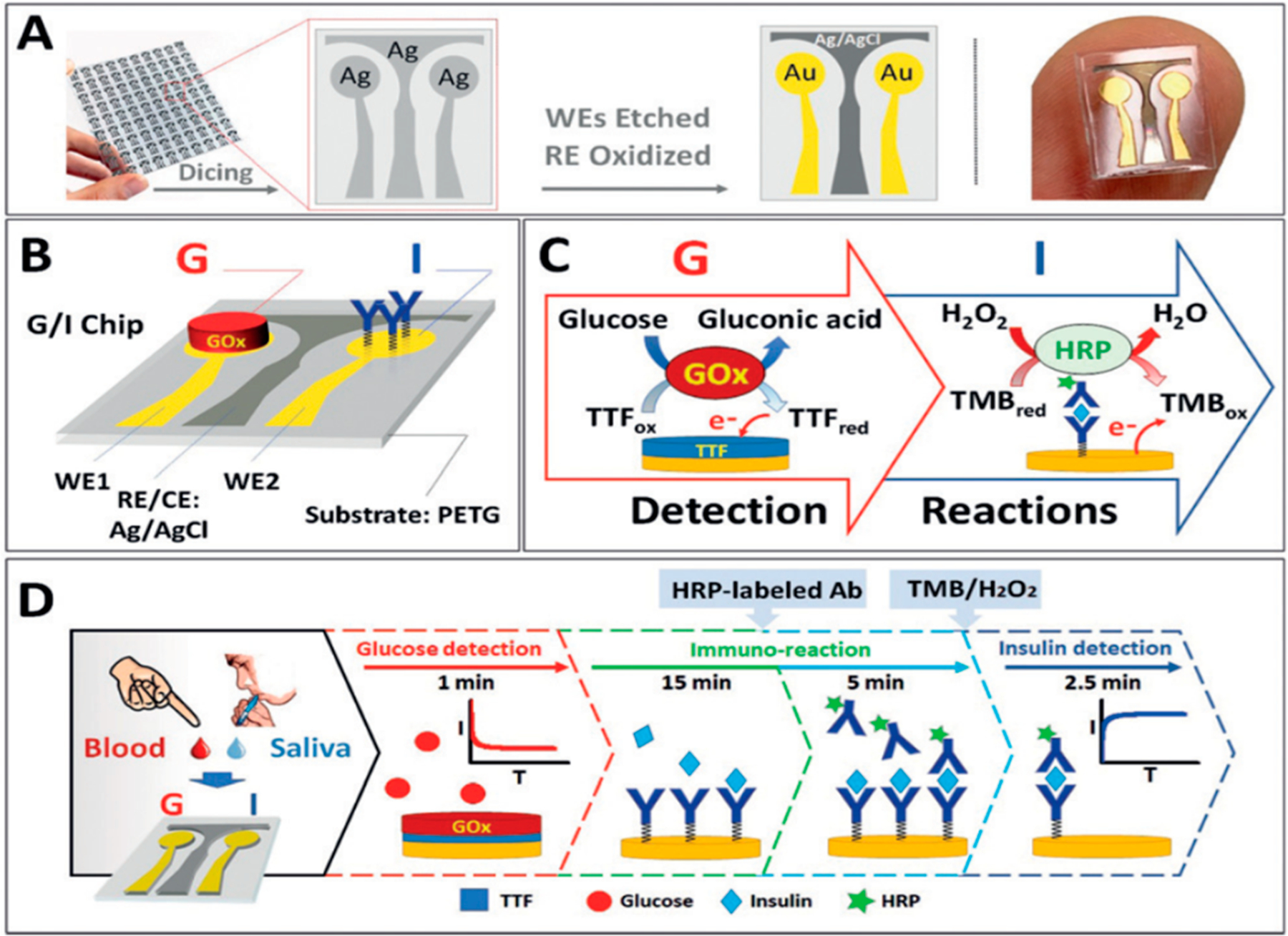
Dual G/I biosensor chip. (A) The G/I sensor chip array showing the two Au WEs for glucose and insulin biosensors, with Ag/AgCl electrode reference. (B) Localized detection of G and I on a sensor chip, showing the immobilized GOx and insulin antibody bioreceptors. (C) Recognition and redox processes in G/I sensing. Glucose detection is amperometric +0.2 V on AuWE1 with TTF-mediated biocatalytic (GOx) oxidation of G. Insulin is detected on Au WE2 at @0.1 V by sandwich immunoreaction assay by measuring H2O2 reduction current catalyzed HRP and mediated by 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). (D) Glucose is measured followed by 15 min sample incubation and subsequent 5 min incubation with HRP-labeled antibody. Finally, insulin is monitored after washing the chip and adding mediator and H2O2. Reproduced from Enzymatic/Immunoassay Dual-Biomarker Sensing Chip: Toward Decentralized Insulin/Glucose Detection, Vargas, E.; Teymourian, H.; Tehrani, F.; Eksin, E.; Sánchez-Tirado, E.; Warren, P.; Erdem, A.; Dassau, E.; Wang, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Vol. 58, Issue 19 (ref 28). Copyright 2019 Wiley.
