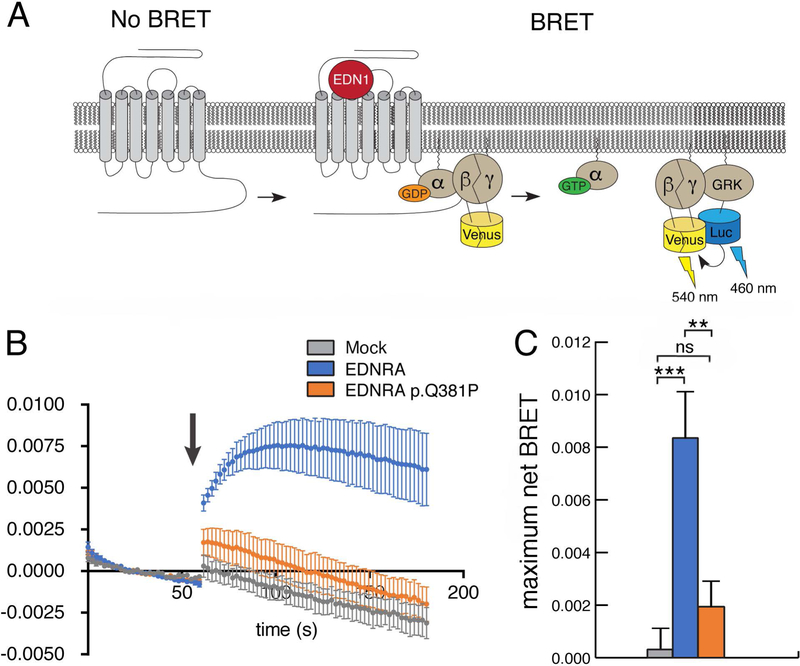
Figure 4. The EDNRA p.Q381P variant disrupts G protein activation.
(a) Schematic for the G protein activation BRET reporter assay. EDN1-induced EDNRA activation promotes dissociation of the G protein heterotrimer to Gαq and Gβγ-Venus. Subsequent interaction of Gβγ-Venus with mas-GRKct-nLuc produces BRET, which is an indirect reporter of G protein activation. (b) BRET assay in HEK293T cells transfected with the BRET components shown in (a) and empty vector (mock), wild type EDNRA or EDNRA p.Q381P. Baseline BRET was measured for 30 seconds, at which time cells were treated with EDN1 (indicated by arrow) and measured for another 2 minutes. A robust EDN1-induced BRET response was observed only in cells expressing wildtype EDNRA (blue trace). In the presence of EDNRA p.Q381P (orange trace), BRET was not statistically different from the presence of a mock vector (grey trace). Traces represent the average delta BRET of at least three independent transfections. Error bars at each timepoint represent SEM. (c) Maximum BRET response was quantified as the average of maximum delta BRET values elicited by EDN1. Assays were performed in triplicate at least three times. Error bars indicate SEM; two-tailed t-test; **p < 0.01, ***p< 0.005; n.s., not significant.