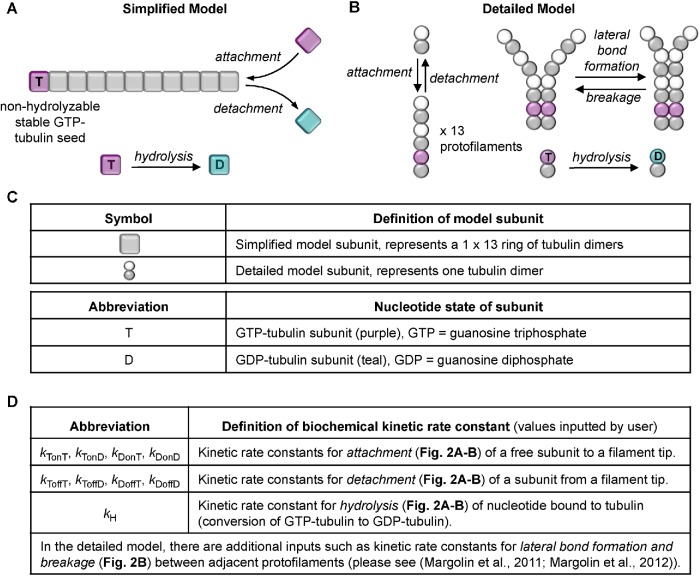
FIGURE 2:
Processes that occur in the computational models. (A) In the simplified model, MTs are approximated as simple linear filaments that can undergo three processes: subunit addition, loss, and hydrolysis. Addition and loss can occur only at the tip. Hydrolysis can occur anywhere in the filament where there is a GTP subunit. (B) In the detailed model, there are 13 protofilaments, each of which undergoes the same processes as in the simplified model but also undergoes lateral bonding and breaking between adjacent protofilaments. (C) Information about the subunits in the models. In both models, the kinetic rate constants (panel D) controlling these processes are input by the user, and the MTs grow off of a user-defined constant number of stable MT seeds (composed of nonhydrolyzable GTP–tubulin). The standard DI parameters (Vg,Vs, Fcat, Fres; see Figure 1, E and F) are emergent properties of the input rate constants, [free tubulin], and other aspects of the environment, such as the number of stable seeds. For more information about the models and their parameter sets, see Box 1, Materials and Methods, Gregoretti et al. (2006), and Margolin et al. (2011, 2012).