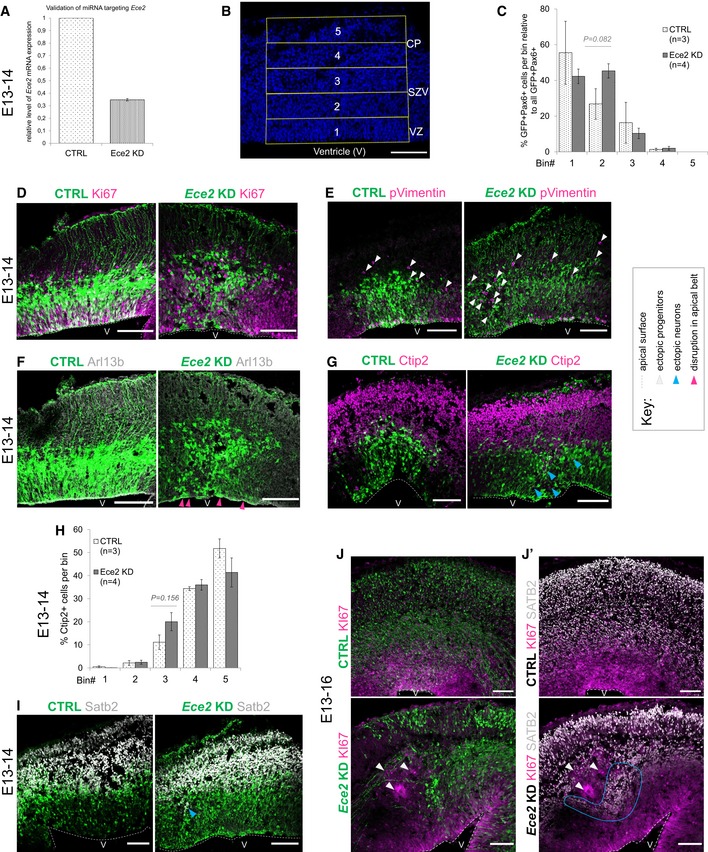
Figure EV2. Ece2 KD in vivo leads to changes in apico‐basal polarity and in progenitor and neuron positioning.
-
AValidation of microRNA targeting Ece2 by qPCR reveals a KD efficiency of about 65% relative to control mRNA levels.
-
BBinning strategy of brains at 1 dpe: Division of the thickness of the developing cortex into five equally sized bins from VZ to CP.
-
C–I1 dpe upon Ece2 KD, proliferative progenitors acquire ectopic positions (C–E). Some deep layer (G and H) and upper layer (I) neurons show the same tendency. (C) Quantification of distribution of Pax6+‐transfected progenitors upon Ece2 KD relative to CTRL shows tangential shift to bin2 (n = 3 CTRL and 4 Ece2 KD brains; P = 0.082 in one‐way ANOVA; data shown as mean ± SEM). (H) Quantification of ectopic deep layer neurons at 1 dpe shows trend to ectopic, less basal position upon Ece2 KD (n = 3 CTRL and 4 Ece2 KD brains; P = 0.156 in one‐way ANOVA; data shown as mean ± SEM). (F) aRG morphology is changed, and the apical surface shows patches lacking apically localised Arl13b at 1 dpe.
-
J, J’Example images at 3 dpe showing delaminated ectopic progenitors form rosettes and nodules.
