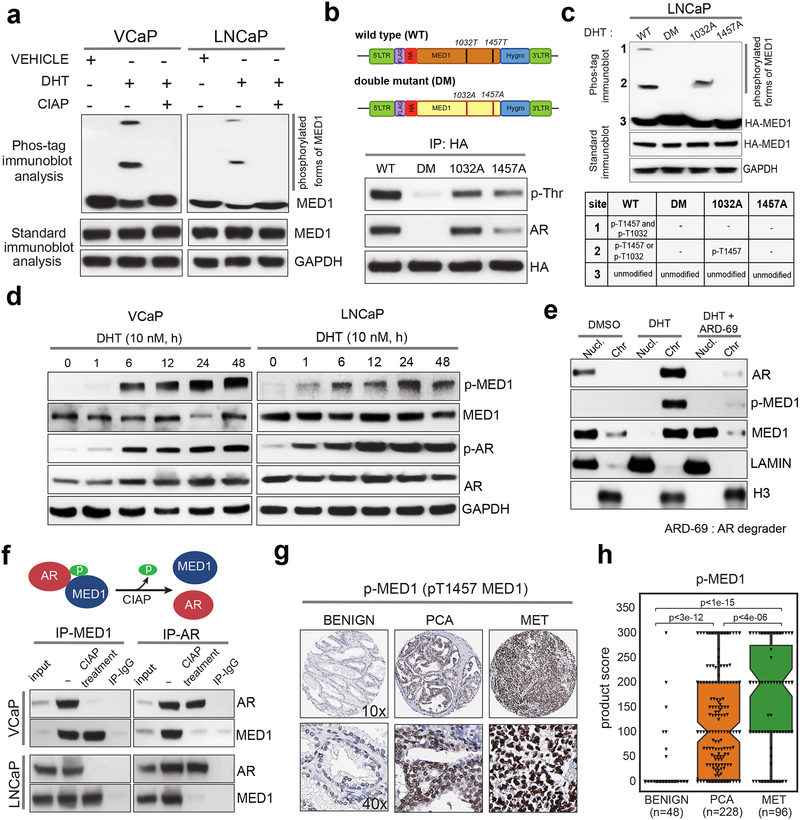
Figure 2 │. MED1 undergoes phosphorylation upon androgen stimulation and is recruited to AR bound enhancers and super-enhancers.
(a) MED1 phosphorylation upon activation of AR signaling. Cells were stimulated with DHT, and nuclear fractions were treated with or without calf intestine alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) before Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting for MED1. Control immunoblots were done on normal gels with the indicated antibodies. (b) Top, Illustration of the FLAG/HA‐tagged wild-type (WT) MED1 and threonine-phosphorylation site T1032A/T1457A double‐mutant (DM) MED1. Bottom, Immunoprecipitation of HA‐tagged WT MED1, single and double mutant MED1 in LNCaP cells. Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti‐HA antibody followed by immunoblot analyses using anti‐phospho‐threonine and anti-AR antibody. (c) LNCaP Cells grown in CSS containing media were transfected with HA-tagged wild-type (WT), double mutant (DM), T1032A or T1457A mutant MED1 plasmids for 48h followed by stimulation with DHT for 12h. The nuclear proteins were extracted and used for Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and standard immunoblotting with HA antibody. The table below indicates the identity of bands present on the phos-tag blot. (d) Immunoblot analyses showing time dependent increase in p-MED1 (p-T1457 MED1) levels by DHT stimulation in VCaP and LNCaP cells. (e) Chromatin and soluble nuclear fractions extracted from LNCaP cells grown in CSS containing media for 48h and subsequent stimulation with DHT alone for 12h or DHT for 6h followed by 6h treatment with ARD-69 (100 nM) were used to probe the indicated proteins. LAMIN and total H3 served as controls for nuclear and chromatin fractions respectively. (f) Top, Schematic depicting phosphorylation dependent MED1-AR interaction. Bottom, LNCaP cells were starved and stimulated with DHT, the nuclear proteins obtained were employed for reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (g, h) Tissue microarray analysis of p-MED1 in Benign, PCA (primary), and MET (metastatic) prostate tissues and quantification of their product scores.