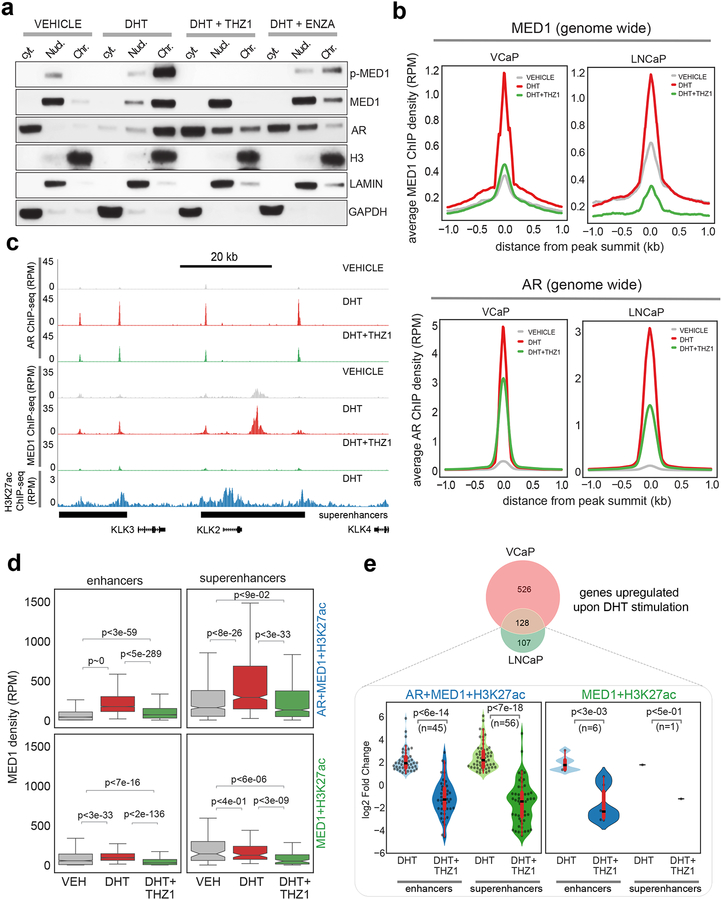
Figure 4 │. CDK7 inhibition by THZ1 disrupts co-recruitment of MED1 and AR to the chromatin.
(a) Immunoblot analysis demonstrating the loss of chromatin bound MED1 (p-MED1) upon THZ1 treatment. Chromatin, nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions from LNCaP cells grown in CSS containing media for 3-days following stimulation with DHT in the absence/presence of 100 nM THZ1 for 6h were used to probe the indicated proteins. Enzalutamide at 5 μM was used as a direct anti-AR. (b) Genome-wide averaged MED1 and AR ChIP-seq enrichment in VCaP and LNCaP cells grown as in (a). (c) Genome browser tracks of AR, MED1, and H3K27ac binding at the KLK2, KLK3 and KLK4 locus in the indicated condition for VCaP. The super-enhancers (SEs) associated with this region are displayed as black bars at the bottom. (d) MED1 is recruited in a ligand-dependent manner to AR+MED1+H3K27ac regions. Box plots showing MED1 densities (RPM) at AR co-bound and the AR-devoid enhancers and SEs in vehicle, DHT and DHT+THZ1 treated samples. (e) Integrative analysis of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq shows majority of AR target genes associate with AR+MED1 occupied enhancers and SE. (Top) Venn diagram showing 128 genes commonly upregulated upon DHT treatment in VCaP and LNCaP cells. (Bottom) Each of the 128 genes were associated with enhancers and SE regions described in (d) and the change in their expression under different treatment condition is shown as a violin plot. The significance values shown in panels (d) and (e) were computed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test.