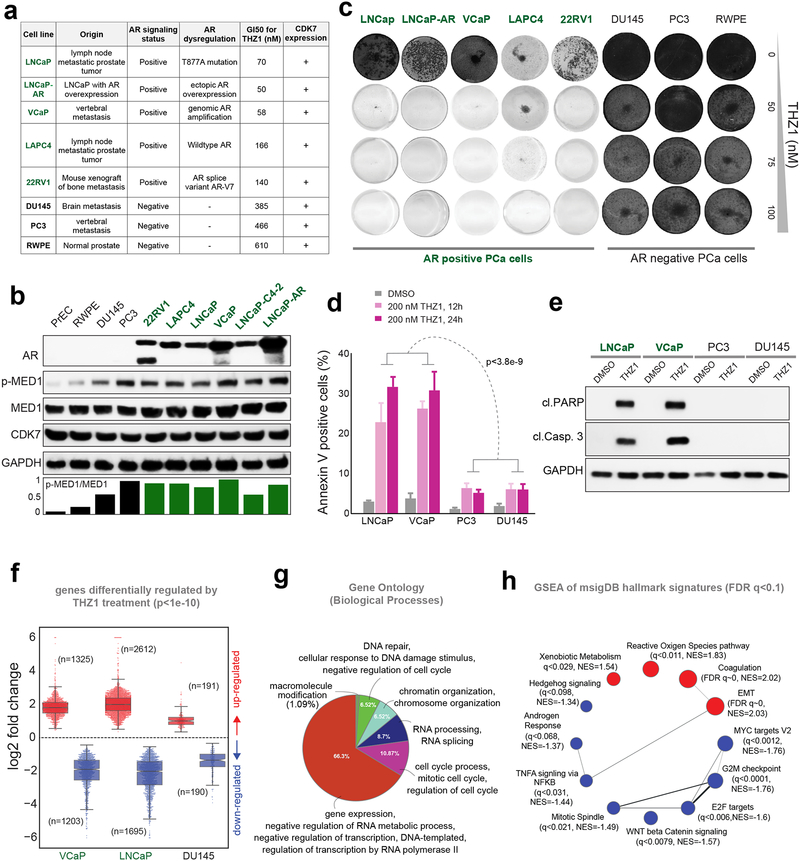
Figure 5 │. Prostate cancer cells with active AR-signaling are sensitive to CDK7 inhibition.
(a) GI50 for THZ1 in a panel of eight PCa cell lines is shown alongside their site of origin, AR status, AR dysregulation, and CDK7 expression. (b) Immunoblot analysis of AR, p-MED1, MED1, CDK7 in six AR positive and four AR negative PCa cell lines, GAPDH was used as the loading control. (c) Colony formation assays in the presence of THZ1. Cells were cultured in the presence or absence of THZ1 for 12–14 days followed by staining. (d) Annexin V-FITC staining showing percentage of apoptotic cells upon THZ1 treatment. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. (e) Immunoblot showing cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 in PCa cells treated with 200 nM THZ1 for 24h. (f) Fold changes of differentially expressed genes determined by RNA-seq in three mCRPC cells treated with 100 nM THZ1 for 24h. (g) Gene Ontology (GO) terms for genes down-regulated, by at least 4-fold, upon THZ1 treatment in VCaP and LNCaP cells. (h) GSEA network plot showing positively (red) and negatively (blue) enriched hallmark signature gene sets, as determined by GSEA with FDR q<0.1, in THZ1 treated VCaP and LNCaP cells.