Fig. 1. LTA is the radioprotective agent in LGG-CM.
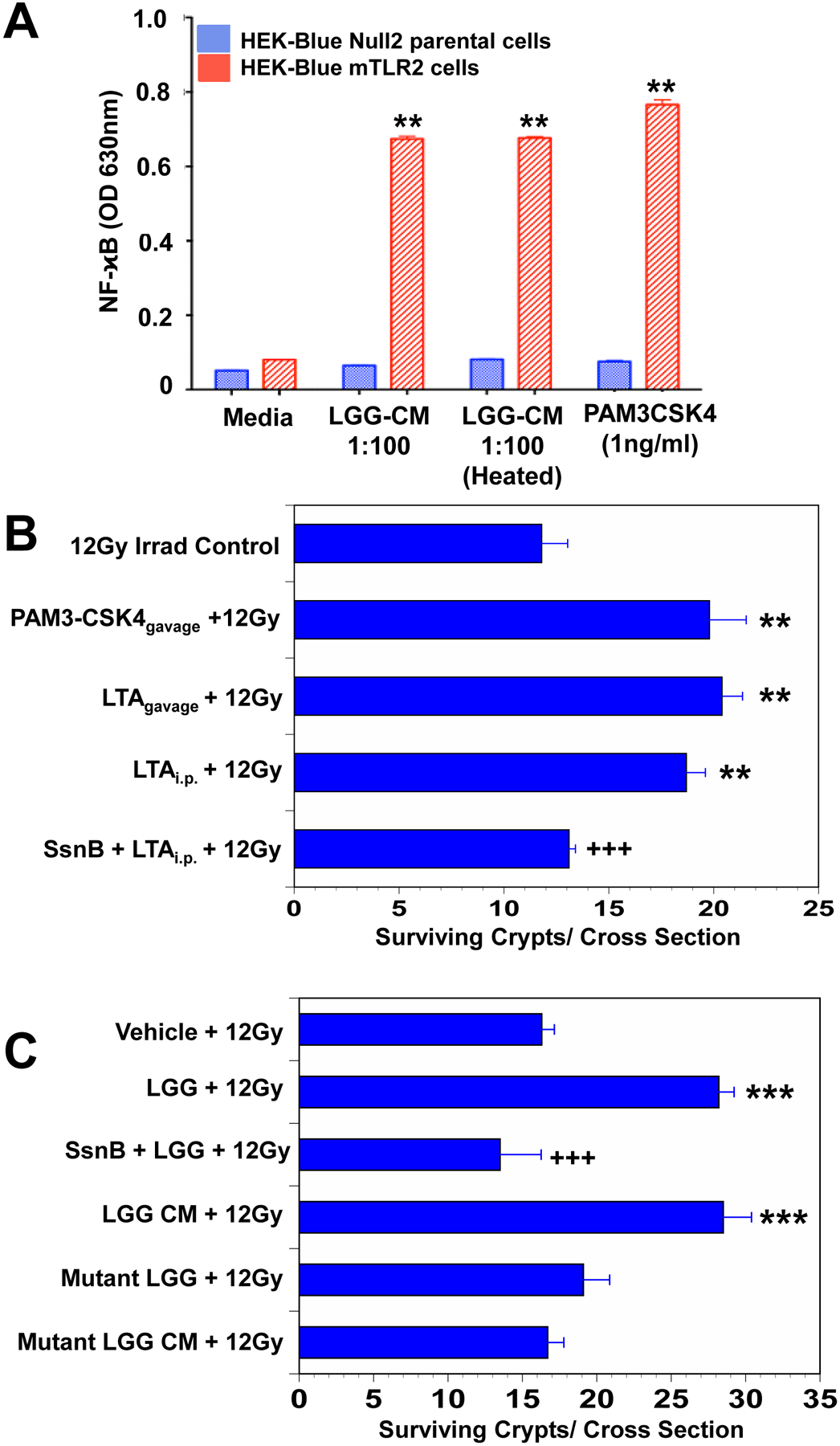
(A) LGG-CM, and the TLR2 agonist PAM3-CSK4 activated NFκB and alkaline phosphatase in HEK-Blue mTLR2 reporter cells. Alkaline phosphatase activation is assessed spectrophotometrically. Data are means ± SEM for 6 samples per treatment group. **P<.001 compared with media controls. (B) Mice pretreated for 3 consecutive days with the TLR2 agonist LTA from Staphylococcus aureus by gavage or by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection, or with the synthetic TLR2 agonist PAM3-CSK4 by gavage prior to receiving 12Gy TBI had significantly improved crypt survival. The TLR2 antagonist Sparstolonin B (SsmB) blocked LTA-induced radioprotection. **P<.001 compared with irradiated control. Data are means ± SEM for 10 mice per treatment group. (C) Mice had significantly improved crypt survival after radiation when pretreated with WT LGG or WT LGG-CM by gavage for 3 consecutive days. SsmBblocked LGG-induced radioprotection. There was no radioprotection in the small intestines of mice pretreated with mutant LGG dltD, which produces inactive modified LTA, or mutant LGG-CM. ***P<.0006 compared with irradiated control. +++P<.005 compared with LTA ip + 12 Gy or LGG+12Gy N=10 mice per treatment group.
