Fig. 1. N truncated iRhom1-ΔN confers TNF resistance as identified by CPR screening.
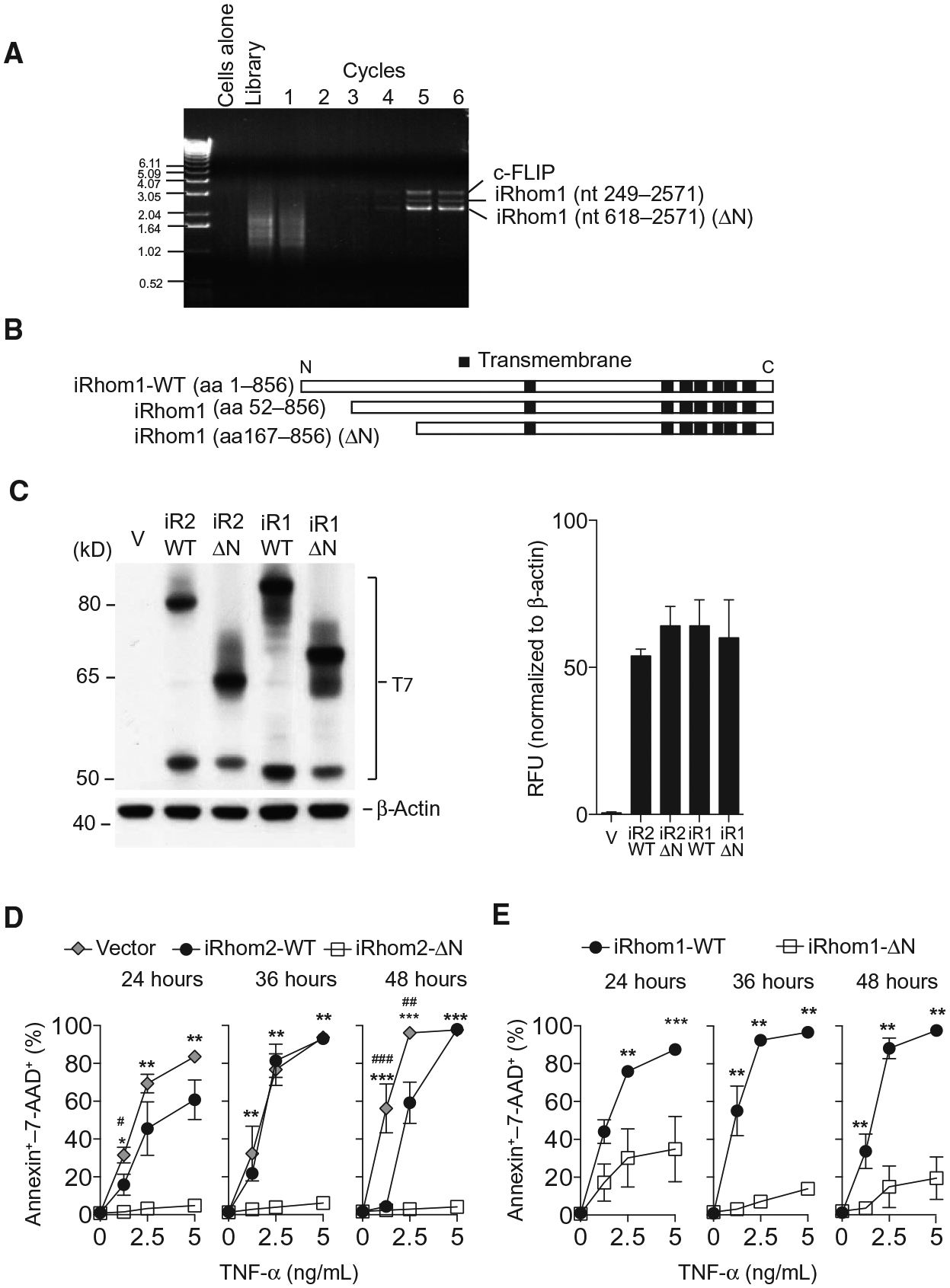
(A) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) results from each round in the CPR screen (see Materials and Methods) showing enrichment for c-FLIP and two short versions of iRhom1 in TNF-resistant cells. (B) Systematic representation of wild-type (WT) and short versions of iRhom1 identified by CPR relative to their predicted transmembrane domain structures. (C) Immunoblotting and densitometry for T7 in lysates from L-929 cells expressing a control vector, T7-tagged WT or ΔN-iRhom1 (iR1) or iRhom2 (iR2) (n = 3). (D and E) Cell death, assessed by annexin V binding and 7-AAD staining using flow cytometry, in 1 × 105 L-929 cells transfected as indicated and treated with recombinant TNF for up to 48 hours (n ≥ 5). Data are means ± SEM from the number of experiments (n) indicated; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 against ΔN; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 against vector. nt, nucleotide; aa, amino acid.
