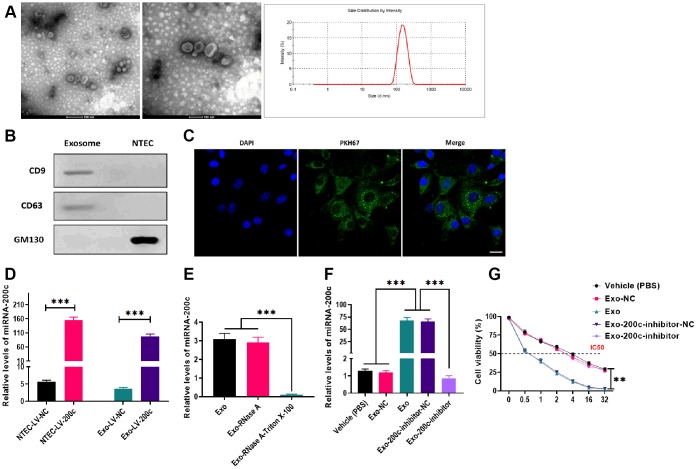
Figure 5.
Characteristics and effects of exosomes derived from normal tongue epithelial cells (NTEC) transfected with miR-200c. (A) The morphology and size distribution of exosomes were determined by electron microscopy and nanoparticle tracking analysis (left figure: scale bars = 200 μm and middle figure: scale bars = 100 μm). (B) The expressions of exosome markers were determined by western blots. (C) The internalization of exosomes was determined by fluorescence assays. Blue: nuclei labeled with DAPI. Green: miR-200c-carrying exosomes labeled with PKH67. (D) The expression of miR-200c was determined by qRT-PCR in NTEC transfected with miR-200c-encoding lentiviral vectors (LV-200c) and their exosomes. (E) The expression of miR-200c was determined by qRT-PCR in exosomes treated with RNase A or the combination of RNase A and Triton X-100. (F) The expression of miR-200c was determined by qRT-PCR in HSC-3DR cells treated with miR-200c-carrying exosomes or miR-200c-carrying exosomes with the miR-200c inhibitor. (G) Cell viability was determined by CCK8 assays in HSC-3DR cells treated with miR-200c-carrying exosomes or miR-200c-carrying exosomes with the miR-200c inhibitor. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.