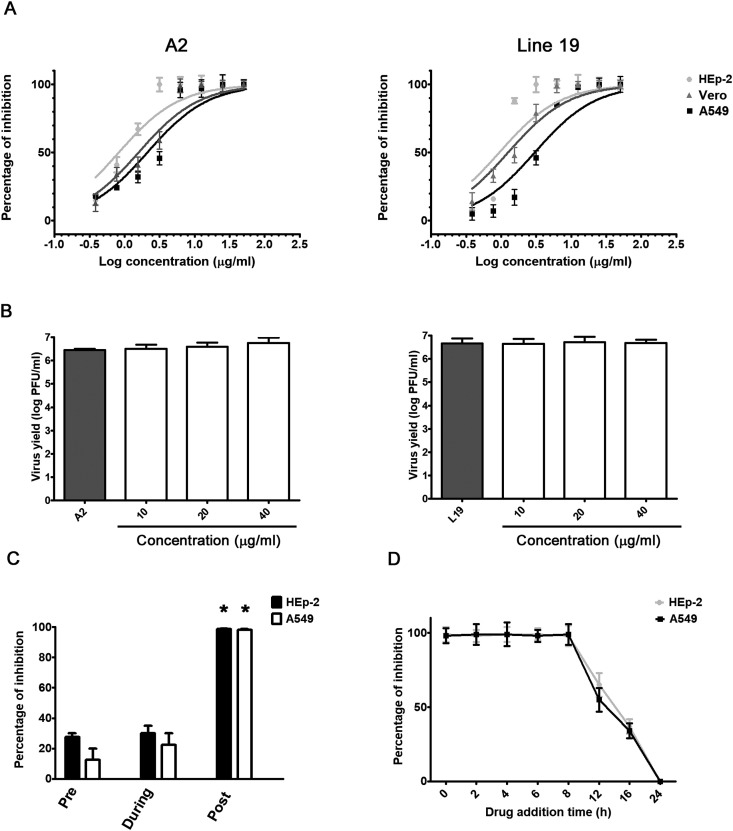
Fig. 2.
Antiviral activity of imiquimod against RSV in vitro. (A) HEp-2, A549 and Vero cells were infected with RSV A2 and line 19 (moi = 1) and treated with different concentrations of imiquimod. After 24 h, total virus yields were titrated by plaque assay in Vero cells. (B) RSV A2 and line 19 were incubated with different concentrations of imiquimod for 2 h at 37 °C. Remaining infectivity was determined by plaque assay in Vero cells. (C) For pre-infection assays, HEp-2 and A549 cells were exposed or not to imiquimod (10 μg/ml) during 2 h, washed with PBS, and then infected with RSV A2 (moi = 1) during 24 h. For co-infection, cells were simultaneously infected with RSV A2 (moi = 1) and treated with imiquimod (10 μg/ml). After 1 h adsorption, the virus-drug mixture was removed, washed with PBS, and compound free medium was added during 24 h. For p.i. assays, cells were infected with RSV A2 (moi = 1) for 1 h, and then treated with imiquimod (10 μg/ml) for 24 h. (D) HEp-2 and A549 cells infected with RSV A2 (moi = 1) were treated or not (CV) with imiquimod (10 μg/ml) at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 16 h p.i. Total virus yields were determined by plaque assay in Vero cells at 24 h p.i and plotted as the percentage of inhibition with respect to untreated–infected control (CV). Data represent mean ± SD for n = 3 independent experiments, performed in duplicate. *Significantly different from CV (p-value <0.05); One way ANOVA with Tukey post test.