Fig. 1. Viral-TRAP enables molecular tagging of alcohol SA–activated mPFC neurons.
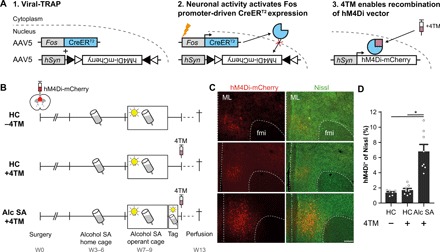
(A) Schematic overview of viral-TRAP. A mixture of AAV-Fos::CreERT2 and Cre-dependent AAV-hSyn::DIO-hM4Di-mCherry was injected bilaterally into the mPFC to enable 4TM-controlled irreversible expression of hM4Di-mCherry. (B) Experimental design for validation of viral-TRAP in the alcohol SA paradigm. All mice underwent acquisition of alcohol SA but were divided into three groups on the “Tag” day. Two groups remained in their home cage (HC) in the absence or presence of systemic 4TM treatment (HC −4TM, N = 6 and HC +4TM, N = 8, respectively). The third group underwent an additional alcohol SA session and received 4TM 2 hours later (Alc SA +4TM; N = 8). Animals were euthanized 4 weeks (W) after the Tag session. (C) Representative images of hM4Di-mCherry expression in the mPFC. ML, midline; fmi, forceps minor of the corpus callosum. Scale bar, 250 μm. (D) Percentage of hM4Di+ cells in the mPFC. Alcohol SA–tagged mice showed increased hM4Di-mCherry expression compared with controls. *P < 0.001. Bar graph, means + SEM.
