Fig. 3. HSV-1 causes reactive gliosis and inflammation reminiscent of neurodegeneration in hiNSCs.
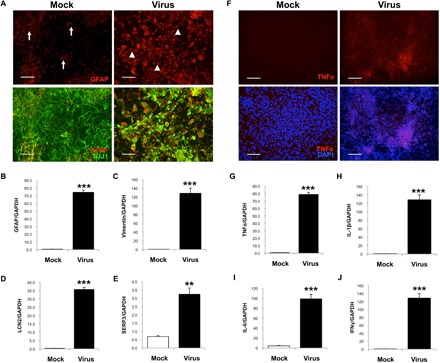
(A and B) HSV-1–infected hiNSCs highly express glia marker GFAP. Immunostaining results reveal increased number of GFAP+ cells and an altered morphology suggestive of gliosis. Other known markers of reactive astrocytes were also up-regulated in HSV-1–infected hiNSCs: (C) vimentin, (D) LCN2, and (E) SERP3. (F and G) Pro-inflammatory marker TNFα was also up-regulated. In HSV-1–infected hiNSCs, qPCR analysis revealed similarly high expression of other inflammatory markers known to be involved in AD: (H) IL-1β, (I) IL-6, and (J) IFNγ. Scale bars, 100 μm. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences with error bars showing means ± SD (**P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001).
