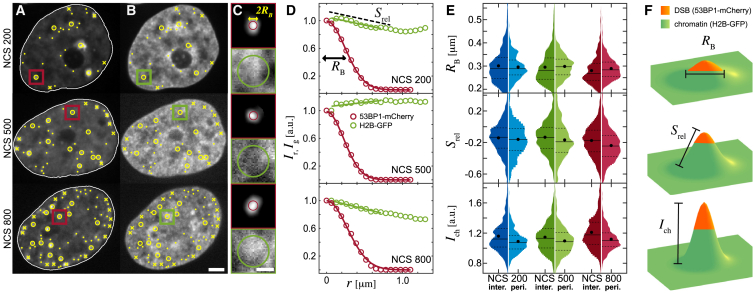
Figure 3.
Local chromatin compaction at DSBs. (A) DSBs detected in 53BP1-mCherry signal are shown: interior DSBs (yellow circles), periphery DSBs (yellow crosses), and untrackable DSBs (yellow dots). (B) DSB positions in H2B-GFP signal are shown (yellow markers). (C) An enlargement of the boxed areas from (A) to (B) is shown. Red boxes show the 53BP1-mCherry signal with the DSB focus size estimated by the red circle. Green boxes show the H2B-GFP signal, and green circle marks an area of 0.75 μm radius around the DSB. (D) Radially averaged intensities of the 53BP1-mCherry (Ir, red markers) and the H2B-GFP (Ig, green markers) signals from (C), normalized by their value at the DSB center, are shown. To determine the 53BP1 focus size RB, a Gaussian was fitted to Ir (red line). To estimate chromatin compaction around a DSB, a line was fitted to Ig over 0.75 μm from the 53BP1 focus center (green line), and its slope Srel was measured. (E) Distributions of RB, Srel, and Ich (H2B-GFP intensity normalized by its mean in a nucleus) for all tracked periphery and interior DSBs are shown. (F) Schematics of RB, Srel, and Ich are shown. Green color corresponds to chromatin, and its height corresponds to the H2B-GFP intensity, which illustrates the chromatin compaction. The red color denotes the size and position of a 53BP1 focus. Scale bars, (A)–(B) 3 μm, (C) 1 μm. To see this figure in color, go online.