Figure 5.
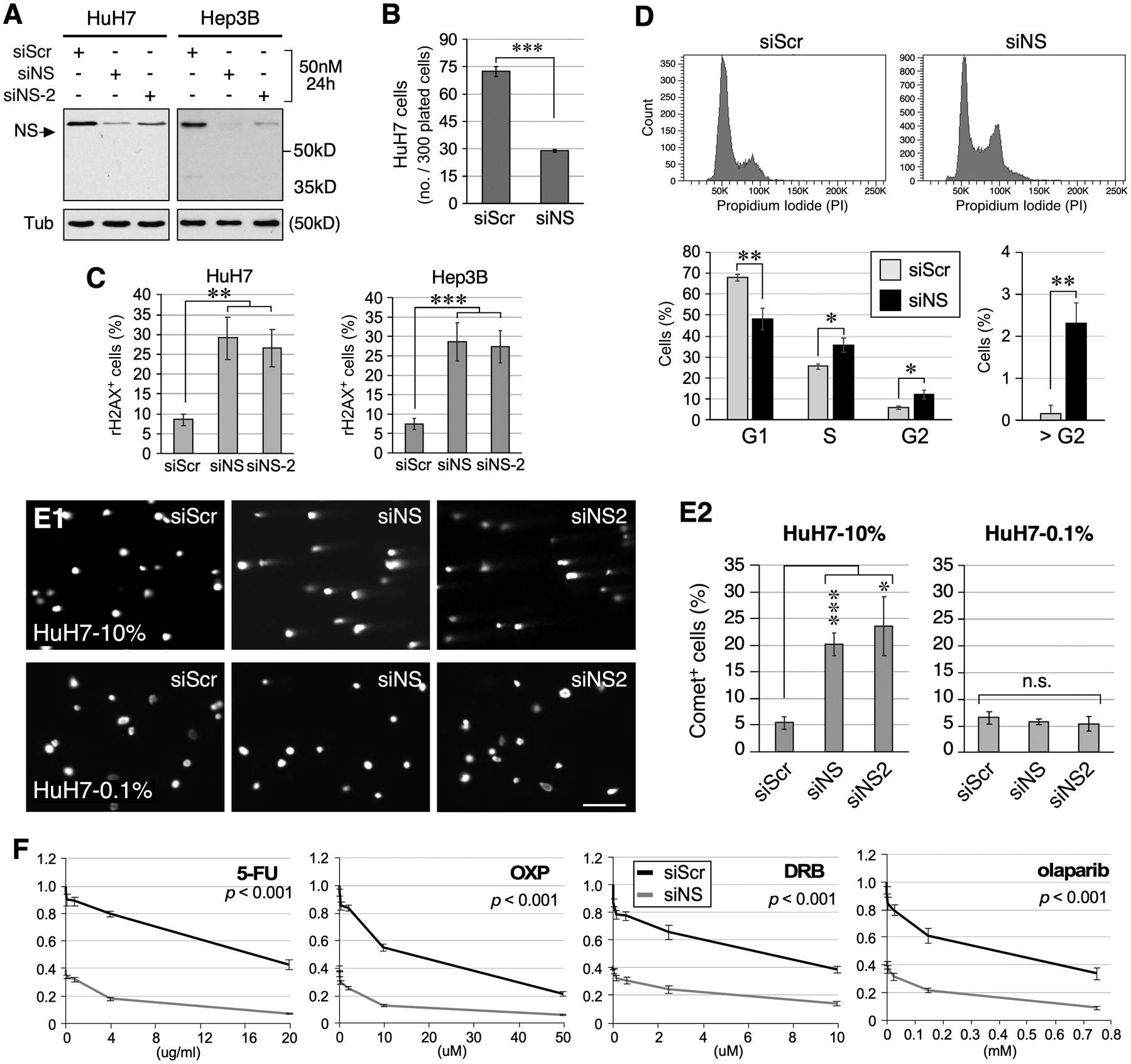
Loss of NS predisposes HCC cells to replication-dependent DNA damage. (A) Western blots of RNAi-treated HuH7 and Hep3B cells. Tub, α-tubulin. (B) Clonogenic survival of RNAi-treated HuH7 cells. (C) Quantitative analyses of γH2AX+ HuH7 and Hep3B cell percentages following RNAi treatment. (D) Cell cycle analysis of Hep3B cells treated with siScr or siNS. Top and bottom panels show representative profiles and statistically analyzed results, respectively. (E) Images and analyses of DNA tail moments of RNAi-treated HuH7 cells under the normal growing (10% FBS) or G0-arrested (0.1% FBS) condition by Comet assay. (F) Dose-dependent curves of clonogenic survival of siScr (black) and siNS (grey) treated HuH7 cells in response to 5-FU, oxaliplatin (OXP), doxorubicin (DRB), and olaparib treatment. Y-axis shows the relative survival compared to the no-drug, siScr-treated group. Significance calculated by two-way ANOVA.
