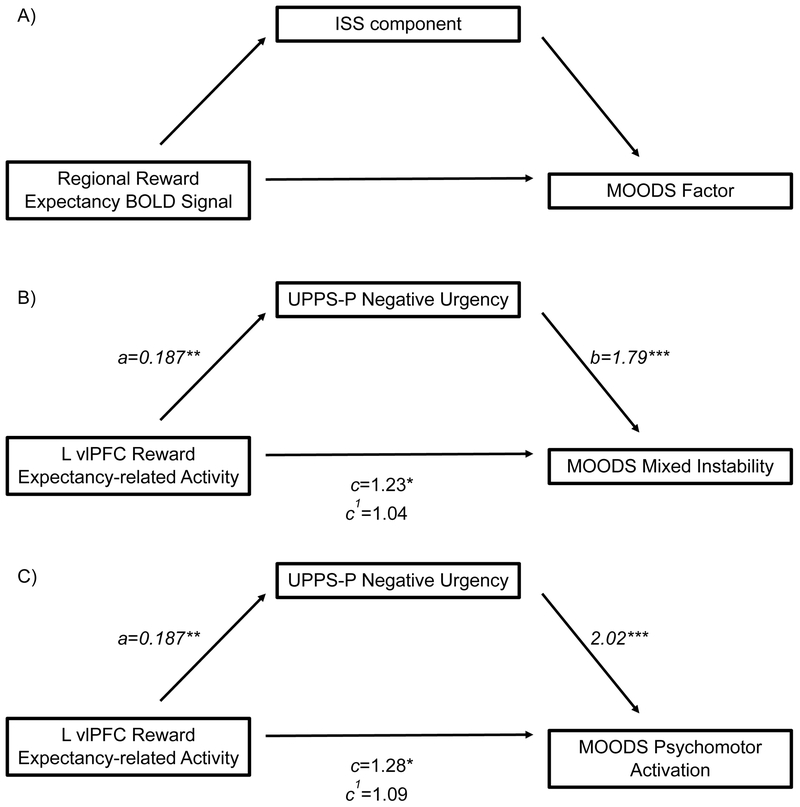
Figure 2.
A) Hypothesized mediation model B) Model for the relationship between reward expectancy-related L vlPFC activity and MOODS Mixed Instability Factor, as mediated by UPPS-P Negative Urgency. The indirect model resulted in an 81.67% reduction in the contribution of reward expectancy-related L vlPFC activity to MOODS factor score versus the direct model. C) Model for the relationship between reward expectancy-related L vlPFC activity and MOODS Psychomotor Activation factor, as mediated by UPPS-P Negative Urgency. The indirect model resulted in a 67.98% reduction versus the direct model. Values represent standardized β for linear regression (a) and IRR for negative binomial regressions (b, c, c1). Percent reductions for IRR are the ratio of change in IRR between the direct and indirect models over the direct model IRR.(79) *p<0.05, **p<0.005,***p<0.0001