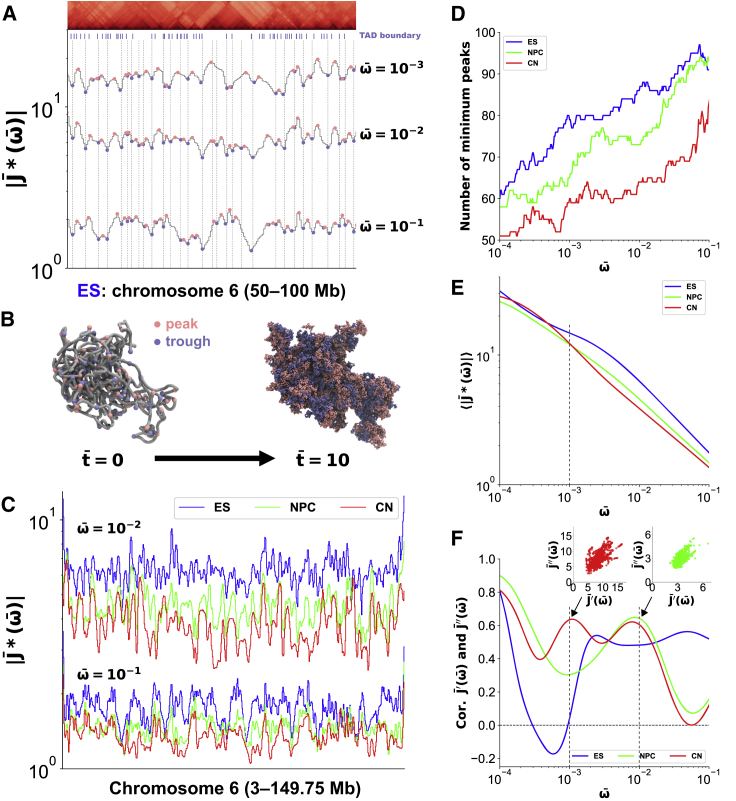
Figure 3.
Complex compliance characterizes chromatin domain boundaries and internal regions during mouse neural differentiation. (A) at = 10−1, 10−2, and 10−3 and a cropped Hi-C contact matrix for the 50- to 100-Mb region on chromosome 6 in mouse ES cells with a TAD boundary profile (8) are shown. Pink and blue dots correspond to peaks and troughs for each curve, respectively. The vertical dashed lines represent the genomic position at the troughs of . (B) A snapshot of an initial polymer conformation (left) in PHi-C simulations for chromosome 6 in mouse ES cells is shown, where pink and blue dots represent the genomic positions at the peaks and troughs of . Also shown is a cumulative plot (right) of the 3D positions of the peaks and troughs in the simulation within time = 10. (C) at = 10−1 and 10−2 for chromosome 6 in mouse ES cells, NPCs, and CN cells is shown. (D) The frequency dependence of the number of minimal peaks as the troughs on for chromosome 6 in mouse ES cells, NPCs, and CN cells is shown. (E) The frequency-dependent average values of along chromosome 6 in mouse ES cells, NPCs, and CN cells are shown. (F) The frequency-dependent Pearson’s correlation between the normalized storage and loss compliances, and , on chromosome 6 in mouse ES cells, NPCs, and CN cells is shown. The scatter plots at = 10−2 and = 10−3 for NPCs and CNs are displayed, respectively. To see this figure in color, go online.