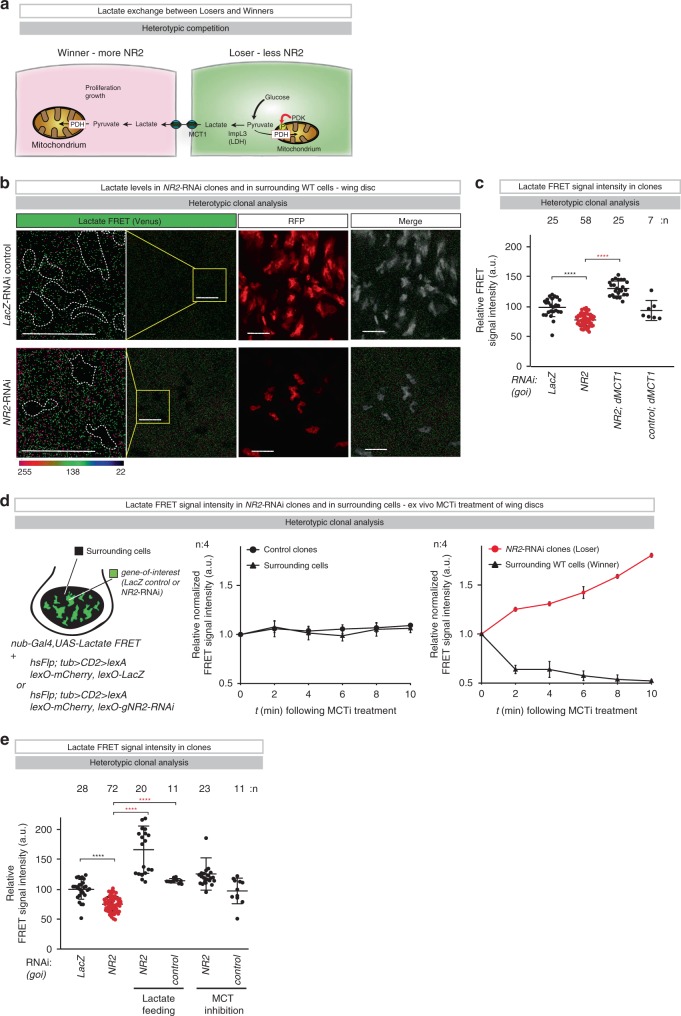
Fig. 4. Loser cells transfer their lactate to winners.
a Schematic model of NR2-dependent regulation of lactate-mediated metabolic coupling during cell competition. b Heterotypic clonal analysis. The indicated genes-of-interest (goi) were knocked down. Lactate FRET signal was monitored in clones and in surrounding cells in the wing pouch. Clones are outlined with dashed lines and marked by RFP (red). Scale bars 20 μm. For genotypes see Supplementary Table 1. Experiments were repeated three independent times. c Heterotypic clonal analysis. The indicated genes-of-interest (goi) were knocked down. Lactate FRET signal was monitored in clones and in surrounding cells in the wing pouch. Diagram shows the relative FRET signal intensity of the indicated RNAi clones per wing pouch ± SD. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.1 by two-tailed Mann–Whitney nonparametric U-test. n depicts the number of wing discs. For genotypes see Supplementary Table 1. d Heterotypic clonal analysis. Relative normalized lactate FRET signal intensity of clonal cells and surrounding cells of the wing pouch was monitored for 10 min following the administration of MCT inhibitor, ex vivo. Diagrams (error bars) show the average of the relative FRET signal intensity of the indicated clones (control or NR2-RNAi) and that of immediately adjacent wild-type cells per wing pouch, as a function of time ± SD. e Heterotypic clonal analysis. The indicated genes-of-interest (goi) were knocked down. Lactate FRET signal was monitored in clones and in surrounding cells in the wing pouch. Lactate feeding and treatment with MCT inhibitor was conducted as outlined in the Methods section. Diagram (error bars) shows the relative FRET signal intensity of the indicated RNAi clones per wing pouch, using the indicated conditions ± SD. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.1 by two-tailed Mann–Whitney nonparametric U-test. n depicts the number of wing discs. For genotypes see Supplementary Table 1.