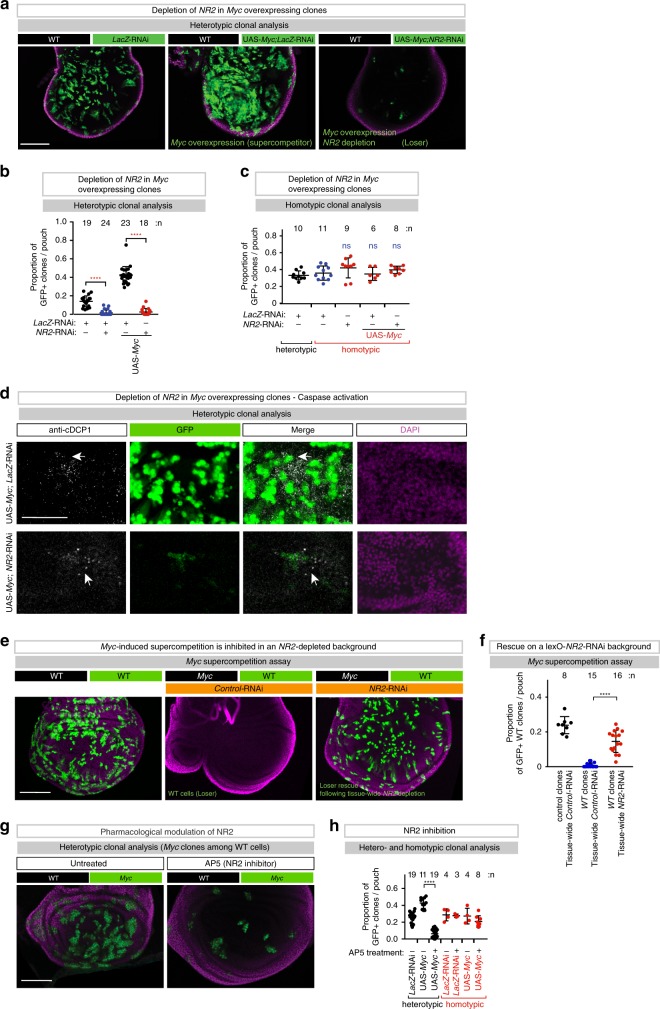
Fig. 8. NR2 is essential for the supercompetitior status of Myc-expressing cells.
a Heterotypic supercompetitor clonal analysis. Myc-expressing clones are marked by GFP. LacZ-RNAi or NR2-RNAi were expressed in clones expressing Myc. Experiments were repeated four independent times. b Quantification of the heterotypic supercompetitor clonal assays. c Homotypic supercompetitor assay. Diagram shows the average occupancy of Myc clones on homotypic background. The indicated genes-of-interest were over-expressed (Myc) and knocked-down (LacZ or NR2) throughout the wing pouch. GFP-marked clones represent non-competitive clones. d Shown are confocal images of wing discs that were immunostained with anti-cleaved DCP1. Scale bar 50 μm. e Heterotypic supercompetitor clonal analysis on Control-RNAi or NR2-RNAi depleted backgrounds. Wild-type clones are marked by GFP, among Myc expressing cells. Scale bar 100 μm. f Quantification of the heterotypic supercompetitor clonal assays. See Supplementary Table 1 for genotypes. g Heterotypic clonal analysis in the presence or absence AP5, an inhibitor of NR2. Scale bar 100 μm. h Quantification of the AP5 treatment assay. Error bars represent average occupancy of the indicated clones per wing pouch ± SD. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.1 by Mann–Whitney two-tailed nonparametric U-test. (b,: NR2-RNAi, UAS-Myc vs. NR2-RNAi,LacZ-RNAi P value: 0.1247). n depicts the number of wing discs. Experiments were repeated three independent times, unless stated otherwise. See Supplementary Table 1 for genotypes.