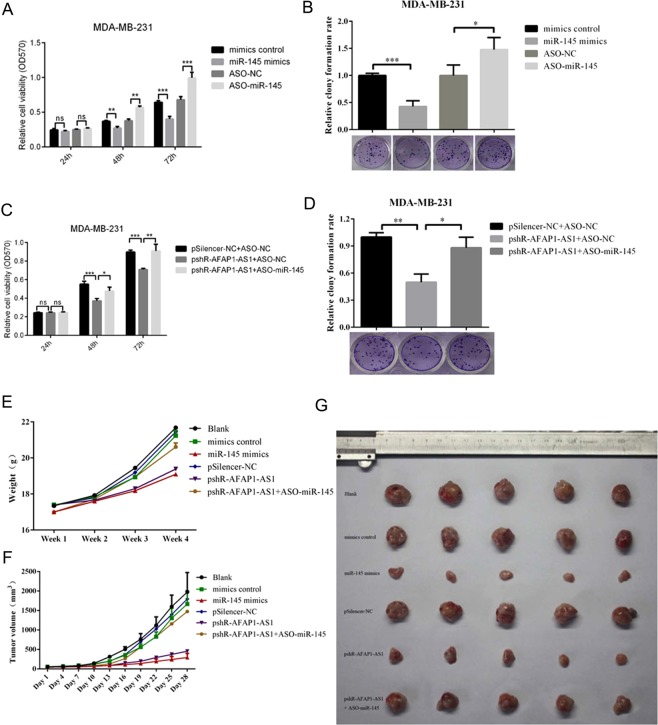
Figure 2.
Differential effects of miR-145 and AFAP1-AS1 on the regulation of breast cancer cell viability and colony formation in vitro and tumor formation in vivo. (A) Cell viability assay. MDA-MB-231 cells were transiently transfected with miR-145 mimics, negative control, ASO-miR-145, or ASO-NC for 48 h, and cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay. (B) Colony formation assay. MDA-MB-231 cells were transiently transfected with miR-145 mimics, negative control, ASO-miR-145, or ASO-NC for 48 h and subjected to a colony formation assay. The graph shows the summarized data from the assay. (C) Cell viability assay. MDA-MB-231 cells were transiently transfected with pSilencer-NC plus ASO-NC, pshR-AFAP1-AS1 plus ASO-NC, or pshR-AFAR1-AS1 plus ASO-miR-145 for 48 h, and cell viability was assessed by the MTT assay. (D) Colony formation assay. MDA-MB-231 cells were transiently transfected with pSilencer-NC plus ASO-NC, pshR-AFAP1-AS1 plus ASO-NC, or pshR-AFAR1-AS1 plus ASO-miR-145 for 48 h before analysis with a colony formation assay. The graph shows the summarized data from the assay. (E) Changes in mouse body weight in nude mouse tumor cell xenograft model. (F) Changes in tumor volume in nude mouse tumor cell xenograft model. (G) Photographs of tumor xenografts. **p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.01.