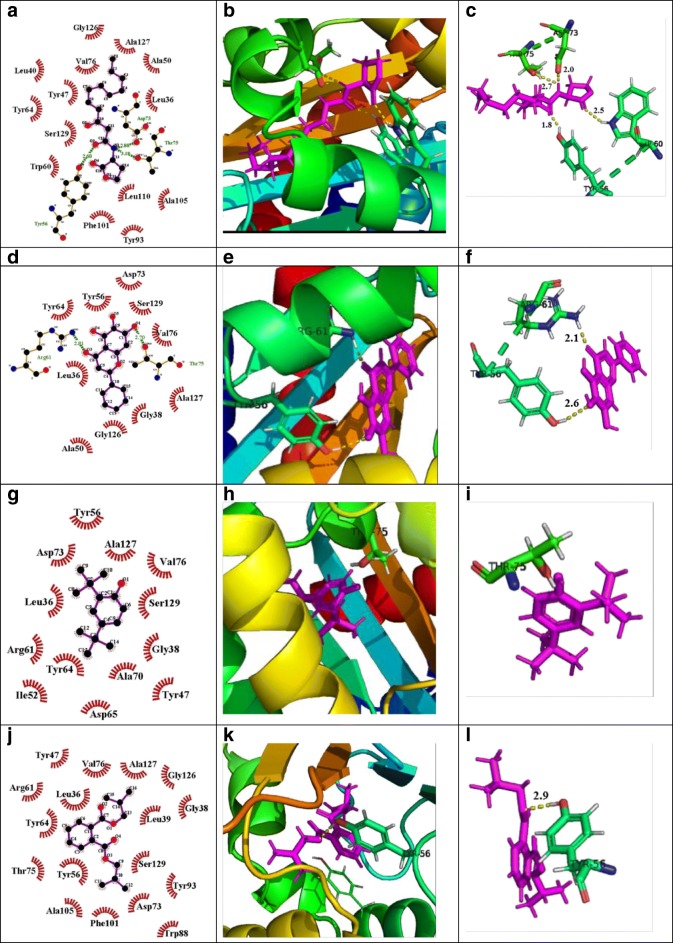
Fig. 7.
Molecular docking studies of phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- and 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester, bioactive components of M. indicus extract to investigate the interaction with the residues of active site of LasR protein, compared with natural ligand and positive control. Here, each ligand protein complex showing three images first one by LigPlot, second one by pymole, and third one by pymole (Zoomed view). (A) LigPlot view of natural ligand (C12-HSL) interacting with active site residues of LasR protein, (B) 3D view of natural ligand-LasR protein complex, (C) zoomed view, (D) LigPlot view of positive control (baicalein) interacting with active site residues of LasR, (E) 3D view of positive control LasR protein complex, (F) zoomed view, (G) LigPlot view of phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- interacting with active site residues of LasR, (H) 3D view of phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-LasR protein complex, (I) zoomed view, (J) LigPlot view of 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester interacting with active site residues of LasR, (K) 3D view of 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid bis(2-methylpropyl) ester-LasR protein complex, (L) zoomed view