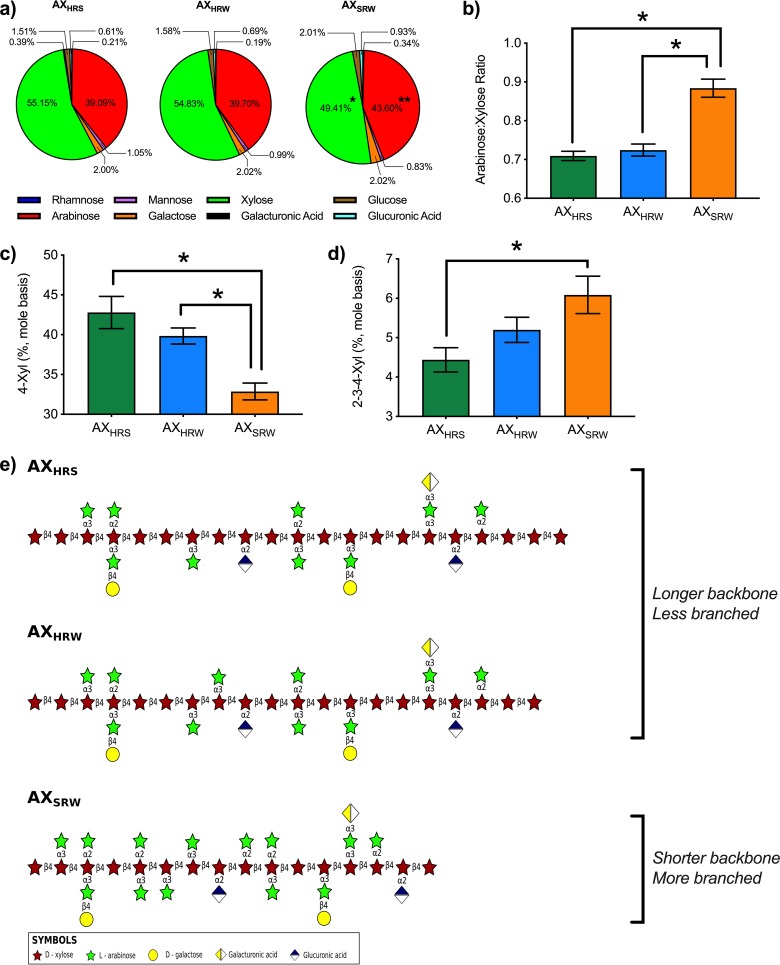
FIG 1.
Compositional and structural features of AXs used. (a) Monosaccharide compositions (mole basis) (*, significantly smaller amount of xylose; **, significantly larger amount of arabinose; two-tailed Student’s t test, P < 0.05). (b) Arabinose-to-xylose ratio (as an indicator of branching density). (c) Relative abundances of 4-Xyl linkage (typical linkage presented in the backbone of AX). (d) Relative abundances of 2-3-4-Xyl linkage (typical linkage presented in the backbone of AX that bear side chains) (other linkages detected are given in Table S1). (e) Schematic of proposed generalized structures of the AX samples drawn based on monosaccharide compositions and linkage profiles. Arabinoxylan extracted from hard red spring wheat (AXHRS) and arabinoxylan extracted from hard red winter wheat (AXHRW) have longer backbones and fewer branching points than arabinoxylan extracted from soft red winter wheat (AXSRW). Statistical analyses were done using two-tailed Student’s t test (P < 0.05). Error bars represent the standard errors of three separate replicates.