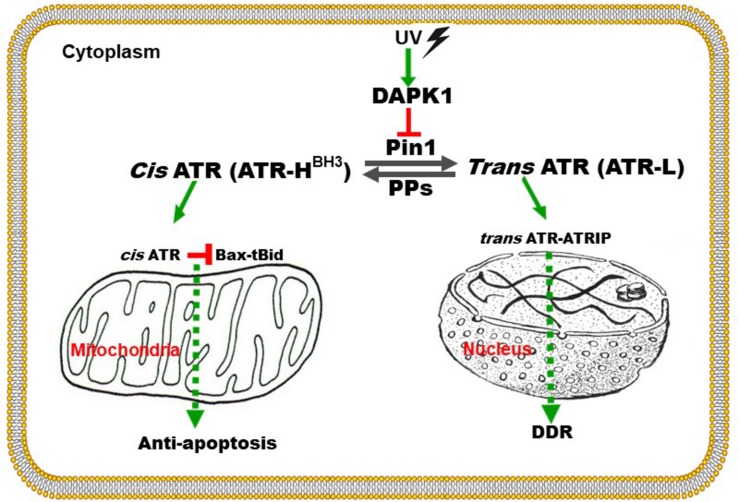
FIGURE 3.
Graphical representation of the proposed mechanism by which ATR plays a direct anti-apoptotic function at the mitochondria. UV damage inactivates Pin1’s isomerization of ATR in the cytoplasm. Cis-ATR (ATR-H) then accumulates and binds to and sequesters t-Bid at the outer mitochondria membrane. Without tBid, Bax and Bak fail to polymerize, thus cis-ATR inhibits cytochrome c release and apoptosis. Trans-ATR (ATR-L) is the dominant isomer in the nucleus where it interacts with ATRIP, RPA and chromatin in the DNA damage repair (DDR) response. PPs (protein phosphatases) can dephosphorylate the Pin1 recognition motif and promote formation of cis-ATR (to be published elsewhere). Modified from Hilton et al. (2015).