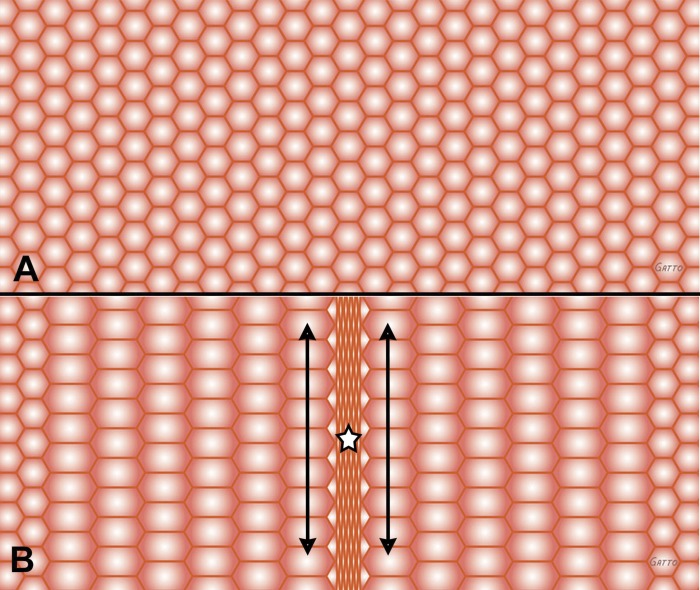
Fig. 3.
Alveoli depicted as hexagons are homogeneously inflated at inspiration (A). Acute lung injury can cause heterogeneous collapse of a group of alveoli during expiration (B, star), while the remaining alveoli remain open. Collapsed alveoli are depicted in the center of the field (B, star). Alveolar instability causes alveoli to open (A, all alveoli homogeneously recruited) and collapse (B, central alveoli collapse causing heterogeneous ventilation) with each breath. Alveolar instability results in excessive dynamic shear stress on alveolar walls of the unstable alveoli (B, star). In addition, alveoli adjacent to the collapsing area are overdistended during expiration with significant dynamic strain during each breath (arrows). These dynamic changes can be seen in Supplemental Animation S3.