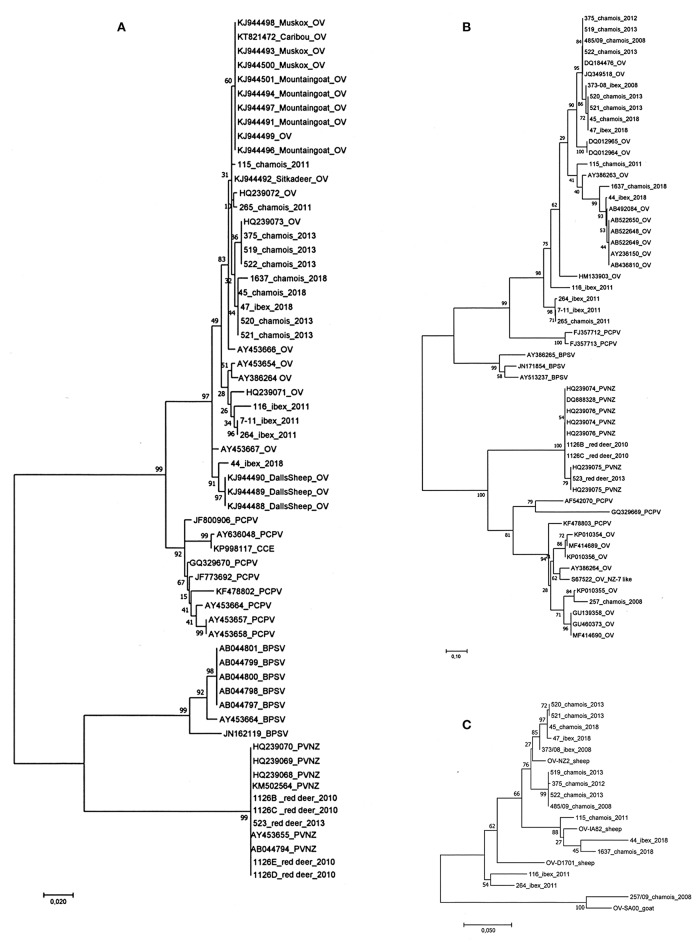
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis performed on the parapoxvirus genes sequenced. (A) The phylogenetic tree of the partial B2L gene of the 22 parapoxvirus samples showing clusters corresponding to the four species of the parapoxvirus genus, all the OV sequences from ibex and chamois cluster with other strains isolated from sheep and goats. Five PVNZ isolates grouped into a separate cluster with other PVNZ. (B) The phylogenetic analysis of the vVEGF showed an expected high variability of the vVEGF variant of isolates from chamois and ibex. The chamois sample 257 grouped with the OV NZ7 like vVEGF variants. (C) Phylogenetic tree based on the concatenated B2L, GIF, vVEGF, and vIL10 amino acid sequences. No host-dependent clustering was identified instead two main clusters of NZ2 and NZ7 OV variants. (OV-NZ-2: GenBank n. DQ184476 OV-IA82 GenBank n. AY386263 D1701 GenBank n. HM133903 OV-SA00 GenBank n. AY386264).