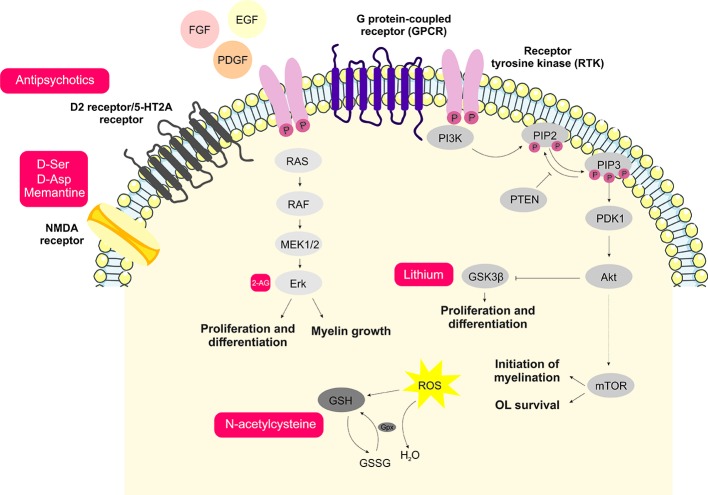
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the main signaling processes and potential novel treatment targets involved with oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia. Antipsychotics acting via inhibition of D2 and 5-HT2A receptors are the main therapeutic strategy currently used in schizophrenia treatment. D-amino acids and memantine are shown here as potential targets aiming for improvements in the glutamatergic signaling dysfunction. Endocannabinoids and the GSK3β inhibitor, lithium, contribute to the MEK/ERK1/2-MAPK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways, which are important for oligodendrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Moreover, aiming to attenuate oxidative damage, antioxidants such as N-acetylcysteine may consist of potential therapeutic agents.