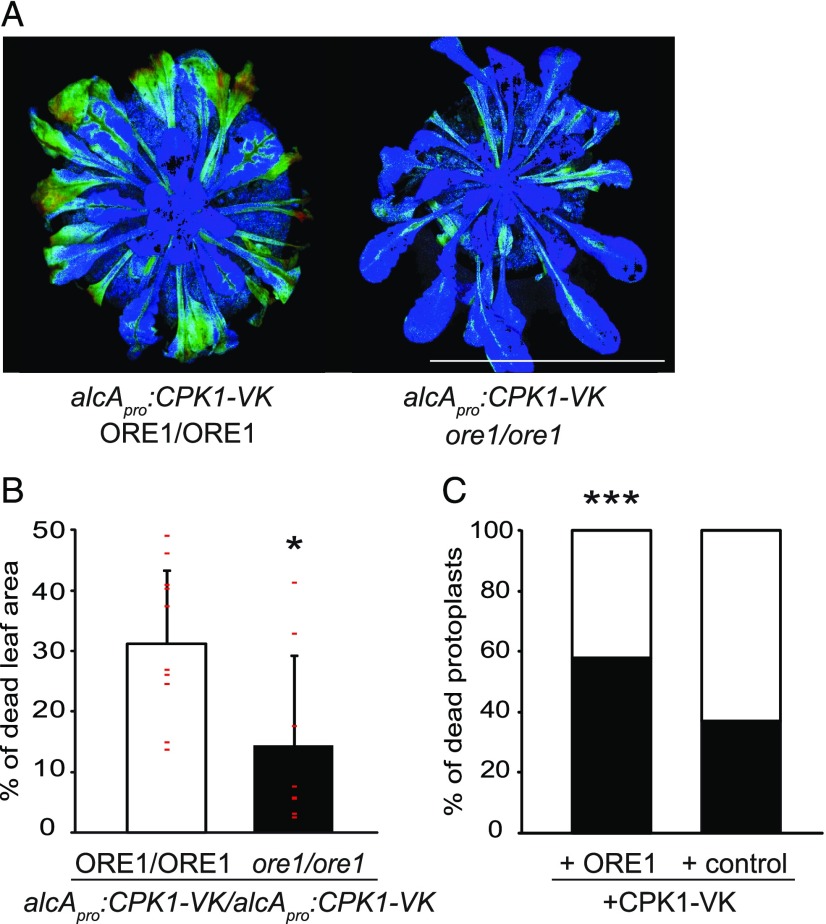
Figure 3.
Induction of Cell Death by Constitutively Active CPK1-VK Requires ORE1.
(A) Five-week-old homozygous alcApro:CPK1-VK plants in either the Col-0 wild type (ORE1/ORE1) or the homozygous ore1-1/ore1-1 mutant background were exposed to ethanol vapor for 12 h. Cell death development was assessed after a further 22 h by chlorophyll fluorescence (PAM) measurements. Leaf areas in light blue, green, or red color (order indicates increasing severity, with red being the most severe) are of reduced photosynthetic activity indicative of cell death, whereas dark blue areas document normal activity. Bar = 3.4 cm.
(B) Quantification of leaf areas with cell death symptoms in (A) was calculated as the percentage of areas of reduced photosynthetic activity (light blue, green, and red) to the total photosynthetically active area. Data show means and SDs. At least eight independent plants were assessed per line. Individual values are depicted as small red horizontal lines. The asterisk indicates a significant difference from the other plant line using the Mann-Whitney U test; *P < 0.05 (Supplemental Data Set).
(C) CPK1-VK-mediated cell death in Arabidopsis leaf mesophyll protoplasts. CPK1-VK was transiently coexpressed with either ORE1 or an empty vector control in protoplasts derived from ore1-1 plants. Both coexpression assays were performed in parallel. The percentage of dying protoplasts (black part of the bars) between the interval of 3 h and 26 h after transfection and the corresponding percentage of surviving cells during the same interval (white part of the bars) were determined by staining with either propidium iodide or fluorescein diacetate for dead and living cells, respectively. Analysis was conducted with a fluorescence microscope. n (total number of cells counted per combination and time point, i.e., 3 h, 26 h) ≥ 165. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from the other coexpression assay. Statistical analysis was done by logistic regression; ***P < 0.001 (Supplemental Data Set).