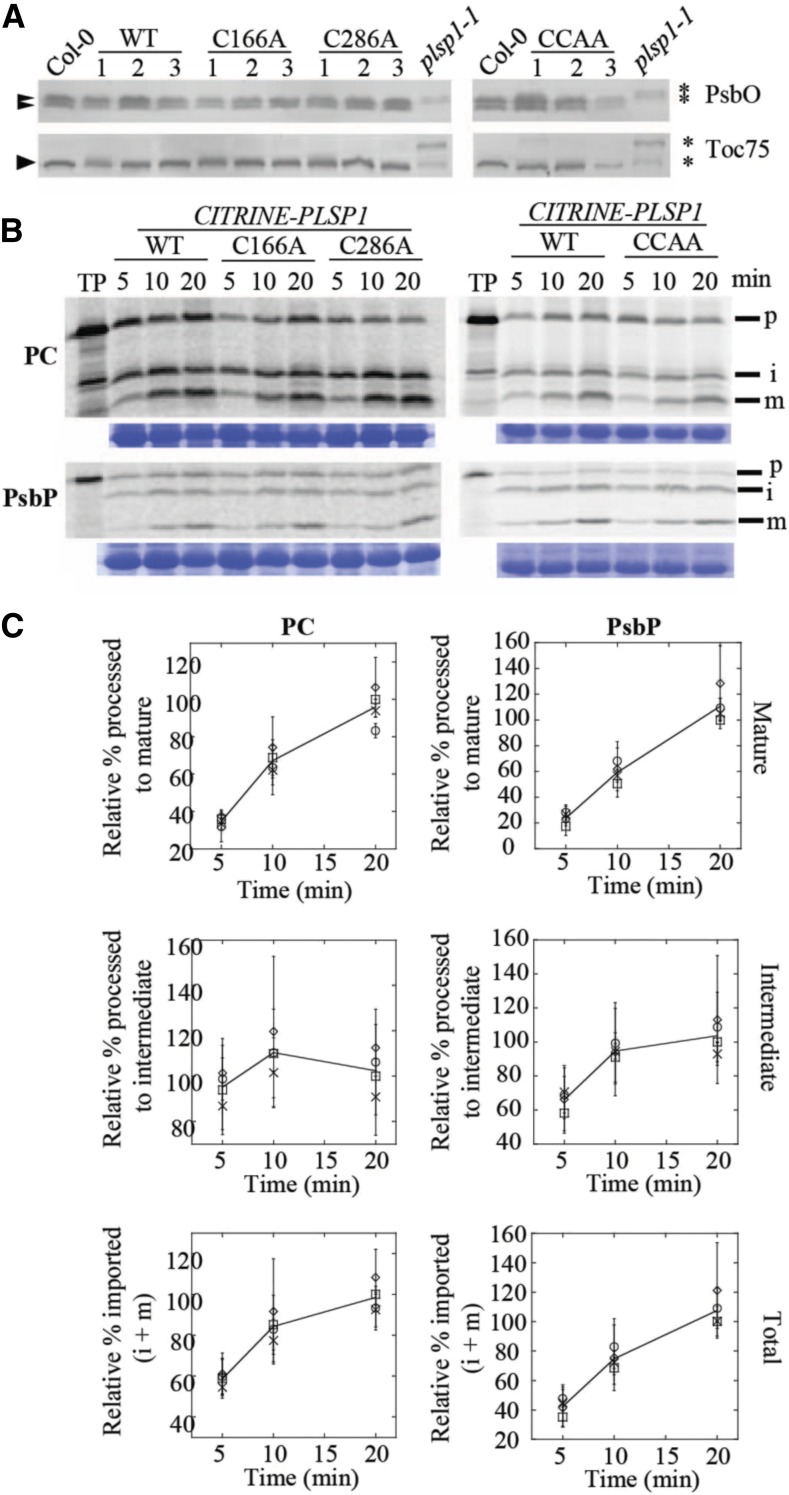
Figure 4.
Citrine-Plsp1-CA Is Active in Chloroplasts.
(A) Size of Plsp1 substrates in chloroplasts isolated from each of the complemented lines shown in Figure 3. Total protein extracts from plsp1-1 null mutants were also used as a control. Proteins were separated on 12% (α-PsbO) or 7.5% (α-Toc75) SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblotting using antibodies stated at the right. Asterisks indicate unprocessed forms, and arrowheads indicate processed/mature form (S) of each protein.
(B) Time course of in vitro import into isolated chloroplasts. 35S-Met-labeled forms of each precursor protein were incubated with isolated chloroplasts for 5, 10, or 20 min. Intact chloroplasts were reisolated through a 35% Percoll cushion and washed once in import buffer. A portion of the recovered chloroplasts was used for chlorophyll quantification to normalize gel loading, and the remainder was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The lines used for the experiments are as follows: C #1, C166A #1, C286A #2, CCAA #2. Each import experiment was repeated three times using chloroplasts isolated on different days. RbcL bands on the Coomassie Brilliant Blue–stained gel are shown below as a loading control. P = precursor; i = intermediate; m = mature; PC, plastocyanin.
(C) Quantification of the import products shown in (B). Bands were quantified relative the corresponding wild type (WT) band at the 20-min time point (i.e., wild-type maximum). Show are the means ± sd of three biological replicates. The line in each graph is drawn through the average among all four lines at each time point. Squares, wild type; circles, C166A; diamonds, C286A; X, C166A/C286A.