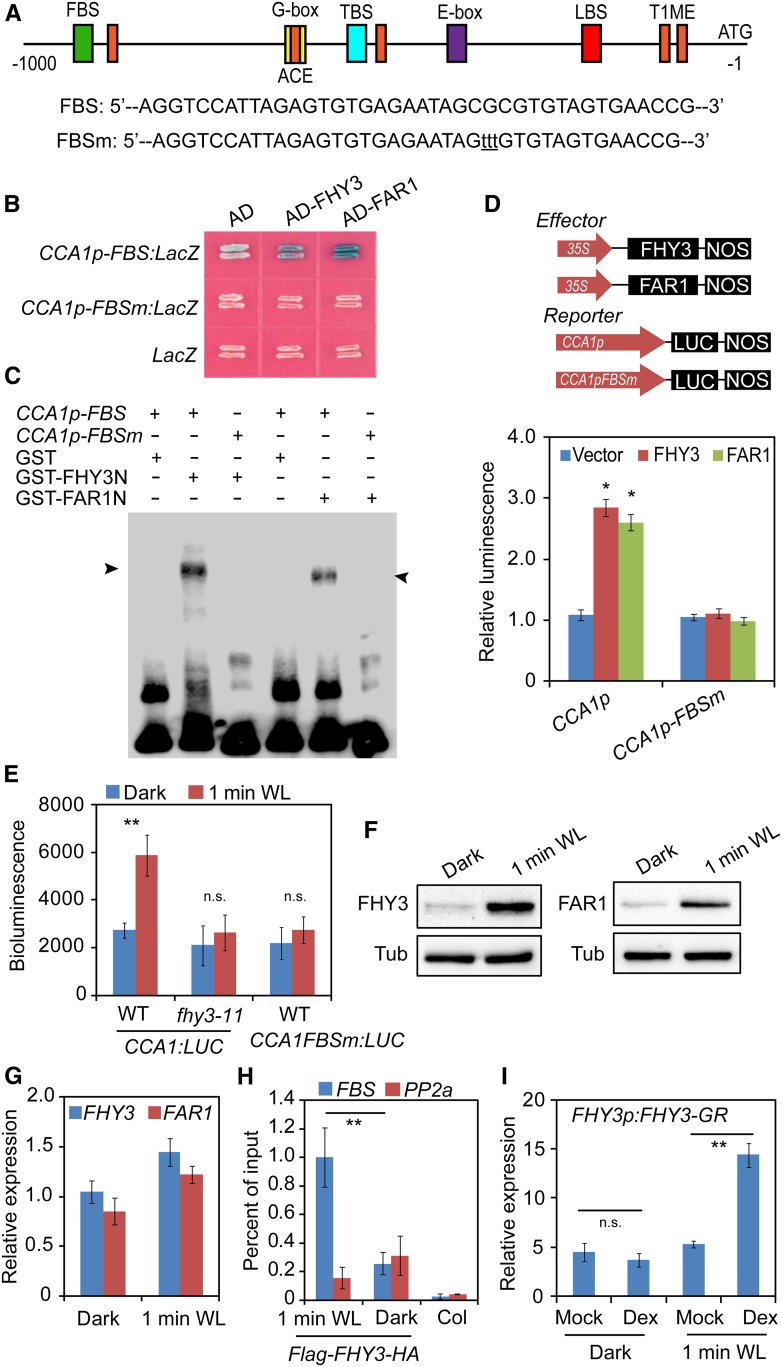
Figure 2.
FHY3 and FAR1 Directly Bind to the CCA1 Promoter and Activate Its Expression.
(A) Schematic representation of the positions and nucleotide sequences of various cis-elements in the CCA1 promoter. The mutations within the FBS element are shown below the diagram in lowercase letters. LBS, LUX binding site; TBS, TCP binding site (CHE binding site); T1ME, TOC1 binding site.
(B) Yeast one-hybrid assay showing that FHY3 and FAR1 directly bind to the CCA1 promoter. The LacZ reporter gene was driven by the CCA1 promoter with a wild-type or mutated FBS element. Mutation of the FBS site in the CCA1 promoter abolished the binding.
(C) EMSA showing that GST-FHY3N (the first 200 amino acids of FHY3) and GST-FAR1N (the first 200 amino acids of FAR1) specifically bind to the biotin-labeled CCA1p-FBS probe. The arrowheads indicate GST-FHY3N and GST-FAR1N.
(D) Transient expression assay showing that FHY3 and FAR1 activate CCA1 expression in N. benthamiana leaf cells (*, P < 0.05, Student’s t test). Values are means ± sd (n = 3 technical replicates). Three independent biological replicates showed similar results.
(E) Bioluminescence assays showing the activities of CCA1 promoters with a wild-type or mutated FBS motif in wild-type or fhy3-11 seedlings (**, P < 0.01, Student’s t test; n.s., no significance). Values are means ± sd (n = 3 technical replicates). Three independent biological replicates showed similar results.
(F) Immunoblot assay showing increased accumulation of FHY3 and FAR1 protein in seedlings treated with 1 min of white light (WL). Five-day-old dark-grown or white light-treated 35S:Flag-FHY3-HA and 35S:Flag-FAR1-HA transgenic seedlings were collected for immunoblot analysis. Anti-Flag antibodies were used to detect the FHY3 or FAR1 protein. Tubulin (Tub) was used as an internal control.
(G) qRT-PCR analysis showing the expression levels of FHY3 and FAR1 in dark-grown or 1-min white light-treated seedlings. Values are means ± sd (n = 3 technical replicates). Two independent biological replicates showed similar results.
(H) ChIP-qPCR assay showing a significant enrichment of FHY3 on the CCA1 promoter by 1 min of white light exposure. The PP2A amplicon was used as a negative control (**, P < 0.01, Student’s t test). An independent biological replicate showed similar results.
(I) qRT-PCR analysis of CCA1 expression in FHY3p:FHY3-GR transgenic seedlings. Five-day-old dark-grown seedlings were treated with 20 μM Dex or DMSO (Mock) for 2 h before being exposed to 1 min of white light (**, P < 0.01, Student’s t test; n.s., no significance). Values are means ± sd (n = 3 technical replicates). Three independent biological replicates showed similar results.