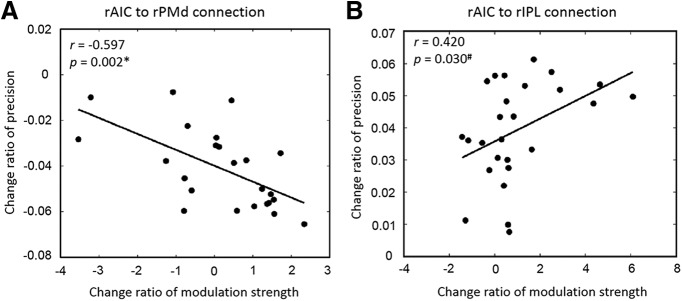
Figure 6.
Correlation between change ratio of prior belief-related effective connections and the precision of prediction error. A, rAIC to rPMd connection. The change ratio is defined by (Wrong-Correct)/Wrong. The stronger the prior belief-related connection strength of rAIC → rPMd was, the lower was the precision of prediction error for unexpected targets. B, rAIC to rIPL connection. The change ratio is defined by (Correct-Wrong)/Correct. A clear trend for a positive correlation (r = 0.420, p = 0.030) was found for expected targets, suggesting that the stronger prior belief related connection strength of rAIC → rIPL was, the higher also the precision of prediction error was. The r and p values are based on a linear (Pearson) correlation analysis.*Significant correlation; #trend level correlation (Bonferroni-corrected (p < 0.025).