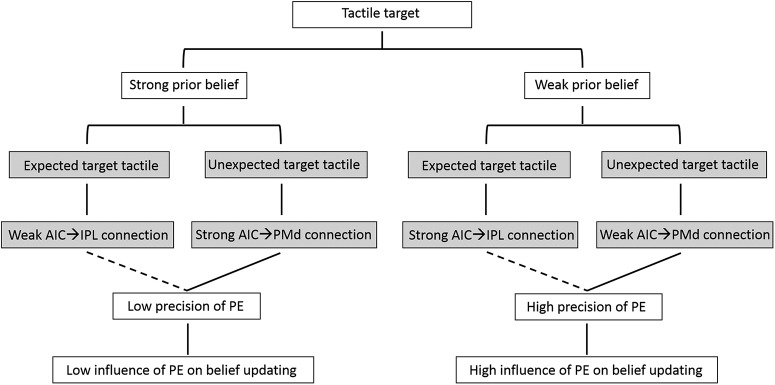
Figure 7.
The schematic summarizes the processing of expected and unexpected targets under different levels of environmental uncertainty (i.e., prior belief). The dashed lines indicate trend level correlation between the connection strength and the precision of PE. Strong prior belief was associated with a low influence of the prediction error on belief updating, especially when the target was unexpected. It also increased the strength of connectivity from the AIC to the PMd on unexpected targets, whereas it decreased the connectivity from AIC to IPL when targets were expected. Tactile targets in combination with weak prior belief were associated with a strong influence of the prediction error on belief updating, again especially for unexpected targets. Weak prior belief also decreased the strength of connectivity from the AIC to the PMd on unexpected targets, whereas it increased the connectivity from AIC to IPL when targets were expected.