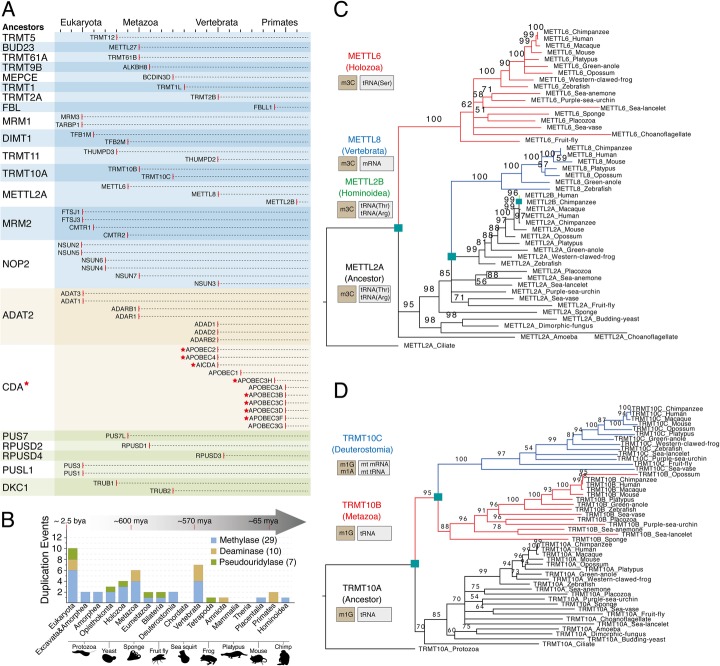
Fig. 1.
Evolutionary analysis of RNA modification “writers.” a Detailed overview of the evolutionary history of RMW duplications during eukaryotic evolution. Red stars indicate that proteins do not target RNAs but they are in the same family with an RNA writer protein. Red lines indicate the evolutionary group in which the enzyme has appeared. b Histogram of RMW duplication events throughout eukaryotic evolution. Duplication events were inferred using multiple sequence alignments, coupled to maximum likelihood tree generation, for each family. c, d Maximum likelihood phylogenetic trees of methyltransferase family METTL2A/2B/6/8 (c) and TRMT10A/B/C (d). Cyan squares indicate the node where the duplication occurred. Numbers shown on the branches indicate bootstrapping values