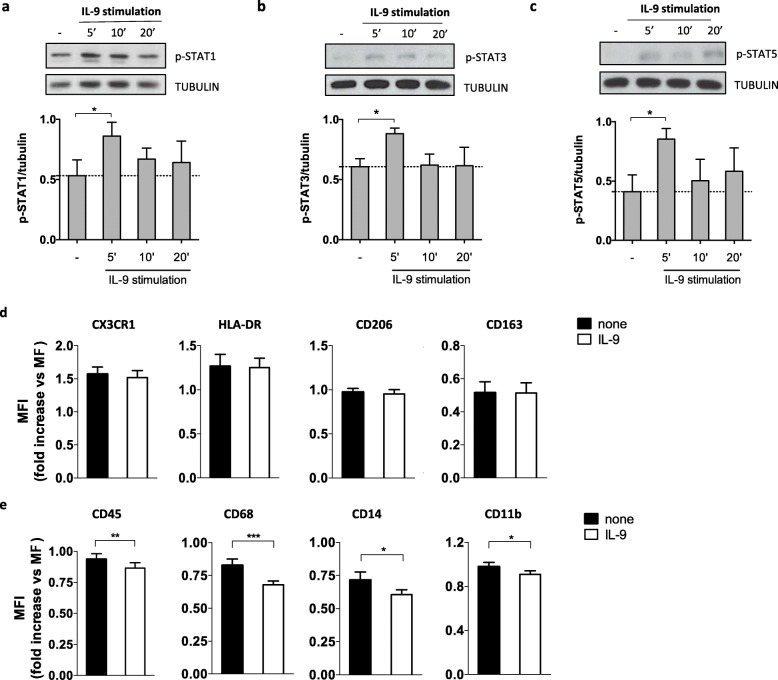
Fig. 5.
IL-9 activates STATs and reduces inflammatory properties in human macrophages. Human macrophages differentiated in vitro from blood classical monocytes were stimulated with IL-9 (200 ng/ml) for 5, 10, and 20 min and compared to unstimulated cells. The phosphorylation of STAT1 (a), STAT3 (b), and STAT5 (c) was analyzed by western blot. Results from a representative donor and cumulative data of 3 donors are reported. Mean ± SEM is shown for each group. *p < 0.05, by paired Student’s t test. Human macrophages differentiated as inflammatory macrophages (Infl. MΦ) from blood classical monocytes of healthy donors (n = 18) were pretreated with IL-9 for 24 h and treated with specific polarizing conditions for 48 h. The expression of CX3CR1, HLA-DR, CD206, CD163 (d), and CD45, CD68, CD14, CD11b (e) was analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are reported as fold change with respect to macrophages (MΦ). Paired Student’s t test was used to compare different conditions. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01;***p < 0.001